
Microneedle patches could speed up diabetic wound healing
www.futurity.org
April 21, 2025, 4:41 p.m.
Growth factors are important for wound healing because they regulate key cellular functions. However, in diabetic wounds, these growth factors are rapidly broken down by other enzymes known as proteases. This dramatically slows down wound recovery. At the same time, diabetic wounds are characterised by persistently high levels of inflammation. We wanted to tackle these two issues by using microneedles for both delivery and extraction. It is minimally invasive, can be fabricated with precision, and allows for the active compounds to be painlessly administered directly into wounds. Microneedle patches are excellent materials for wound healing.
Share on
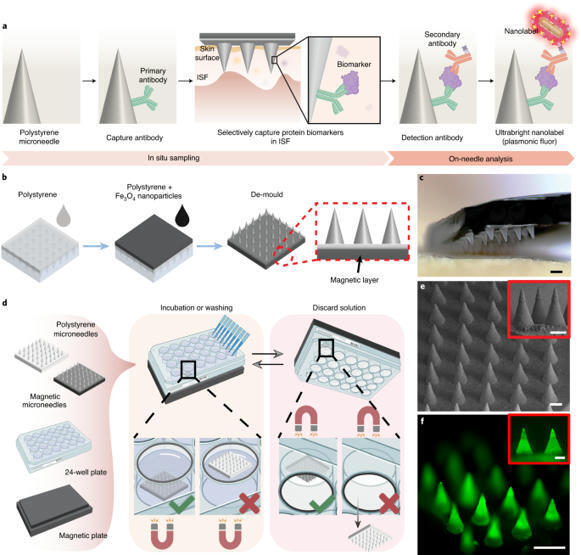
Microneedle patch for the ultrasensitive quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid
www.nature.com
March 12, 2025, 5:51 p.m.
The detection and quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid is hampered by challenges in its sampling and analysis. Here we report the use of a microneedle patch for fast in vivo sampling and on-needle quantification of target protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid. We used plasmonic fluor—an ultrabright fluorescent label—to improve the limit of detection of various interstitial fluid protein biomarkers by nearly 800-fold compared with conventional fluorophores, and a magnetic backing layer to implement conventional immunoassay procedures on the patch and thus improve measurement consistency.
Share on

Silk microneedles could restore wound healing in diabetic patients
www.advancedsciencenews.com
Nov. 4, 2024, 12:19 p.m.
Researchers have developed a new technique to heal wounds using microneedle patches to deliver drugs under the skin. This approach is specifically designed for people with type 2 diabetes, whose injuries often heal slowly or not at all due to their condition.
Share on

Microorganism microneedle micro-engine depth drug delivery
www.nature.com
Oct. 28, 2024, 11:45 a.m.
As a transdermal drug delivery method, microneedles offer minimal invasiveness, painlessness, and precise in-situ treatment. However, current microneedles rely on passive diffusion, leading to uncontrollable drug penetration. To overcome this, we developed a pneumatic microneedle patch that uses live Enterobacter aerogenes as microengines to actively control drug delivery. These microbes generate gas, driving drugs into deeper tissues, with adjustable glucose concentration allowing precise control over the process.
Share on
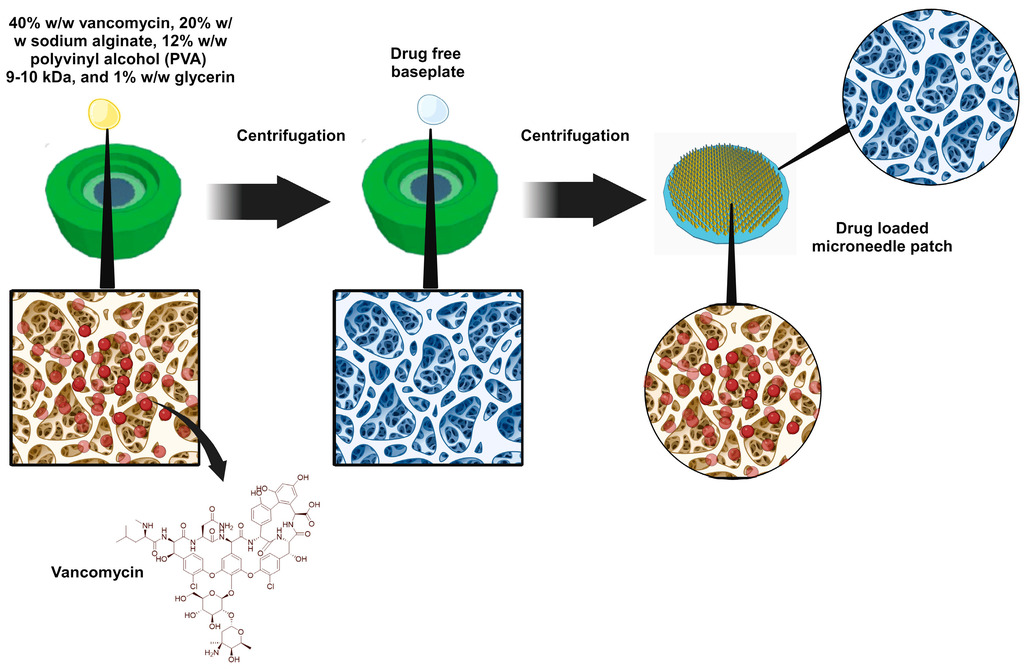
Sodium Alginate Microneedles Loaded with Vancomycin for Skin Infections
www.mdpi.com
Oct. 28, 2024, 11:43 a.m.
In this work, we developed sodium alginate MNs loaded with vancomycin as an innovative approach for treating skin infections, specifically MRSA. Using a double-casting method, we successfully fabricated MNs that exhibited high integrity and were capable of effectively penetrating an ex vivo skin model, as confirmed by light microscopy and mechanical testing. MNs demonstrated substantial drug delivery ability, with 35% of the loaded vancomycin permeated through full-thickness neonatal porcine skin and 10% remaining within the skin after 24 h. This results in an overall delivery efficiency of 45%, indicating the potential of MNs to provide effective dosing for antimicrobial therapy. Furthermore, antibacterial activity tests confirmed the potent effects of the vancomycin-loaded MNs against C. acnes and S. aureus, confirming their suitability as a treatment modality for skin infections.
Share on
Microneedle technology wins Gates grants of $6.6 million
vaccinenation.org
Oct. 28, 2024, 11:40 a.m.
The University of Connecticut (UConn) announced in October 2024 that associate Professor Thanh Nguyen’s research has received “significant” backing from The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The Gates Foundation has awarded a series of grants totalling $6.6 million, following support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the US Department of Agriculture (USDA). The funding will contribute to research and innovation for a microneedle array patch that can deliver multiple human vaccines at once. The Foundation initially awarded $2 million, which has increased after early success.
Share on

Tattoo Ink Found to Be Contaminated With Bacteria
www.medscape.com
July 20, 2024, 12:16 p.m.
When US researchers tested 75 unopened and sealed tattoo and permanent makeup inks from 14 different manufacturers, they discovered that about 35% of the products were contaminated with bacteria. They detected both aerobic bacteria, which require oxygen, and anaerobic bacteria, which thrive in low-oxygen environments like the dermal layer of the skin.
Share on
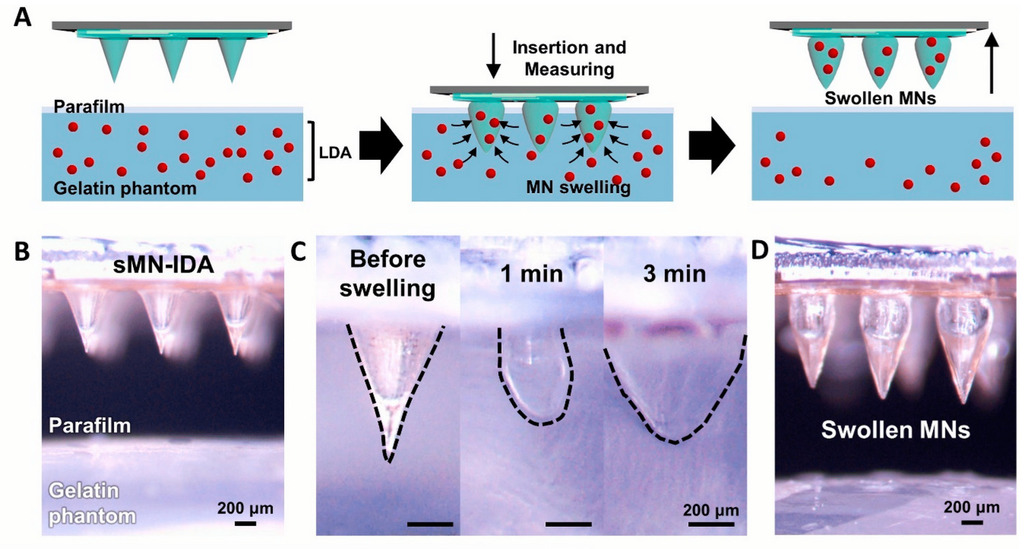
Swellable Microneedles in Drug Delivery and Diagnostics
www.mdpi.com
June 16, 2024, 3:37 p.m.
This manuscript explores the transformative potential of swellable microneedles (MNs) in drug delivery and diagnostics, addressing critical needs in medical treatment and monitoring. Innovations in hydrogel-integrated MN arrays facilitate controlled drug release, thereby expanding treatment options for chronic diseases and conditions that require precise dosage control. The review covers challenges, such as scalability, patient compliance, and manufacturing processes, as well as achievements in advanced manufacturing, biocompatibility, and versatile applications. Nonetheless, limitations in physiological responsiveness and long-term stability remain, necessitating further research in material innovation and integration with digital technologies. Future directions focus on expanding biomedical applications, material advancements, and regulatory considerations for widespread clinical adoption.
Share on
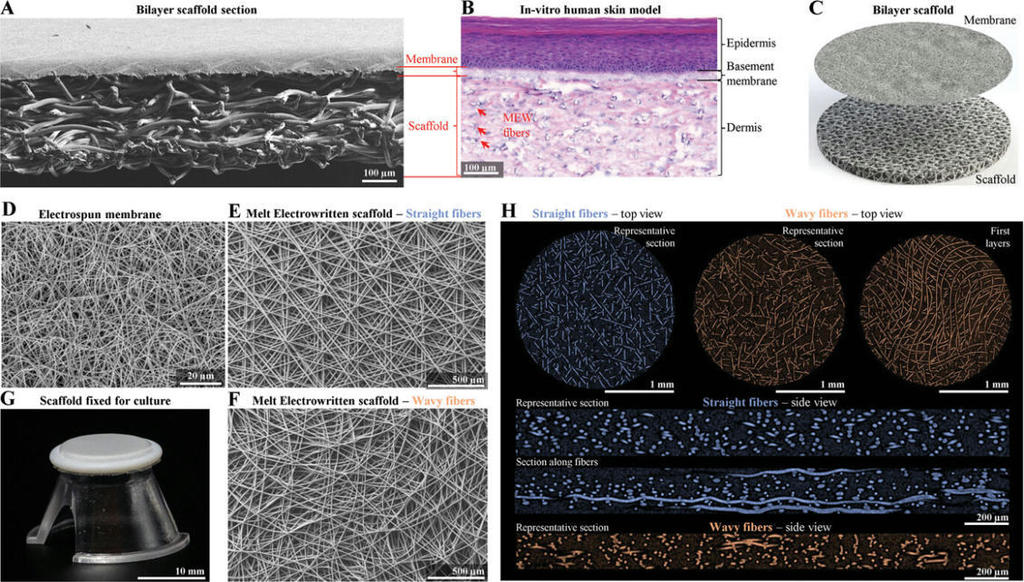
Breakthrough skin model accelerates development for testing and beyond
3dprintingindustry.com
March 31, 2024, 11:38 a.m.
A recent collaboration between researchers at the University of Oregon (UO) and L’Oréal has resulted in the development of a multilayered artificial skin model, designed to resemble the complexity of real human skin closely. This achievement has implications for improving the testing of skin care products and potentially enhancing skin healing methods. Led by Associate Professor Paul Dalton from the Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact at the UO, the research relies on Dalton’s novel 3D printing technique. Published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, this technique enables the creation of a two-layered artificial skin, with each layer separated by a membrane, mirroring the structure of natural skin.
Share on

Recent advances in transdermal drug delivery systems
biomaterialsres.biomedcentral.com
Aug. 25, 2023, 6:23 a.m.
Various non-invasive administrations have recently emerged as an alternative to conventional needle injections. A transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) represents the most attractive method among these because of its low rejection rate, excellent ease of administration, and superb convenience and persistence among patients. TDDS could be applicable in not only pharmaceuticals but also in the skin care industry, including cosmetics. Because this method mainly involves local administration, it can prevent local buildup in drug concentration and nonspecific delivery to tissues not targeted by the drug. However, the physicochemical properties of the skin translate to multiple obstacles and restrictions in transdermal delivery, with numerous investigations conducted to overcome these bottlenecks.
Share on
Rulers Push For mRNA Vaccine Patches To Be Mailed Directly To Homes
www.activistpost.com
July 17, 2023, 6:52 a.m.
The World Health Organization, along with Bill Gates and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are pushing for vaccine patches to be mailed directly to people’s homes. The rulers will stop at nothing to ensure as many humans as possible are injected with mRNA technology and use Big Pharma and its drugs.

Queensland opens needle-free vaccine skin patch manufacturing factory
www.newstarget.com
July 3, 2023, 10:18 a.m.
The vaccine patches being developed by Vaxxas are part of an emerging technology known as microneedle vaccines. This technology offers the convenience of self-administration, enabling vaccine manufacturers to deposit their vaccinations through the surface of the skin in mere seconds. Moreover, the patches can remain stable at room temperature, eliminating the need for cold chain storage.
Share on

Qld’s Vaxxas needle-free vaccine facility three to five years from commercial product
www.news.com.au
June 19, 2023, 1:59 p.m.
Queensland is one step closer to producing needle-free vaccine patches, with biotechnology giant Vaxxas estimating they are three to five years away from releasing their first commercial product. Attending the Hamilton facility’s opening on Monday morning, Deputy Premier Steven Miles said the technology would be a “game changer” to healthcare delivery in Australia and the world.
Share on
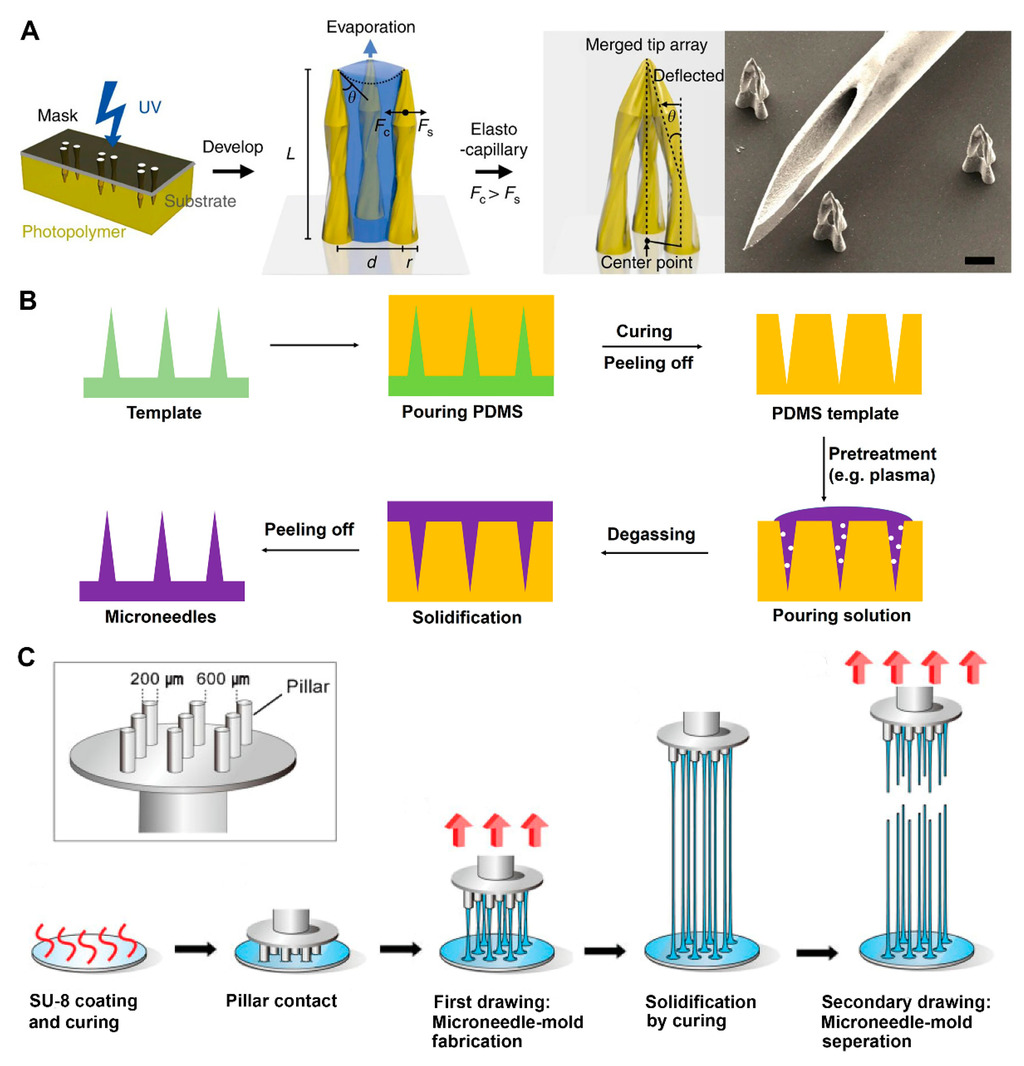
Engineering Microneedles for Therapy and Diagnosis: A Survey
www.mdpi.com
Nov. 28, 2022, 11:07 p.m.
Microneedle (MN) technology is a rising star in the point-of-care (POC) field, which has gained increasing attention from scientists and clinics. MN-based POC devices show great potential for detecting various analytes of clinical interests and transdermal drug delivery in a minimally invasive manner owing to MNs’ micro-size sharp tips and ease of use. This review aims to go through the recent achievements in MN-based devices by investigating the selection of materials, fabrication techniques, classification, and application, respectively.
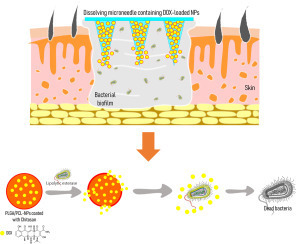
Bacterially sensitive nanoparticle-based dissolving microneedles of doxycycline for enhanced treatment of bacterial biofilm skin infection
www.sciencedirect.com
Nov. 28, 2022, 11:04 p.m.
The presence of bacterial biofilms in wounds is a main issue in the healing process. Conventional therapy of bacterial biofilms is hampered by the poor penetration of antibacterial agents through the physical barrier on the infected skin and the non-specific target of antibacterial agents.
Share on
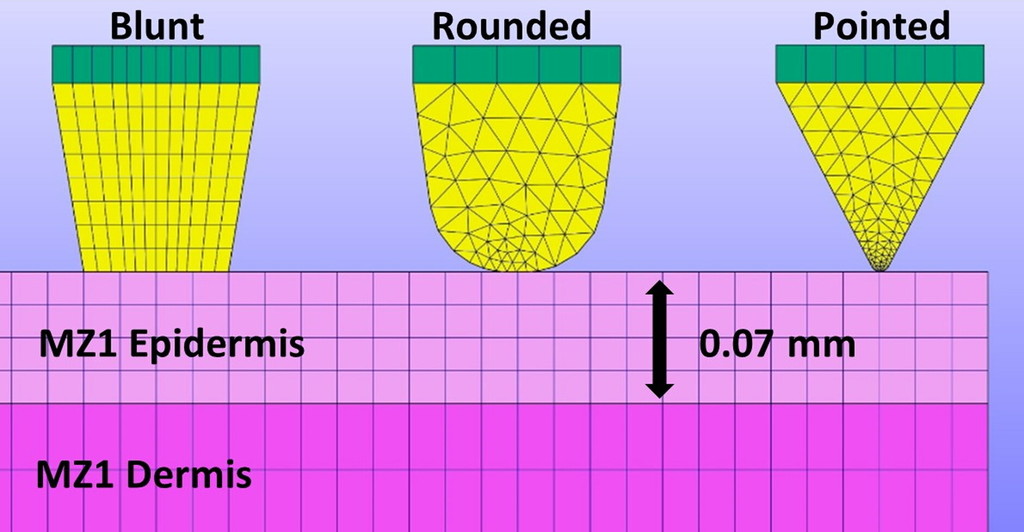
An analysis of the relationship between microneedle spacing, needle force and skin strain during the indentation phase prior to skin penetration
www.tandfonline.com
Nov. 28, 2022, 11:02 p.m.
Microneedle (MN) array patches present a promising new approach for the minimally invasive delivery of therapeutics and vaccines. However, ensuring reproducible insertion of MNs into the skin is challenging. The spacing and arrangement of MNs in an array are critical determinants of skin penetration and the mechanical integrity of the MNs. In this work, the finite element method was used to model the effect of MN spacing on needle reaction force and skin strain during the indentation phase prior to skin penetration. Spacings smaller than 2–3 mm (depending on variables, e.g., skin stretch) were found to significantly increase these parameters.
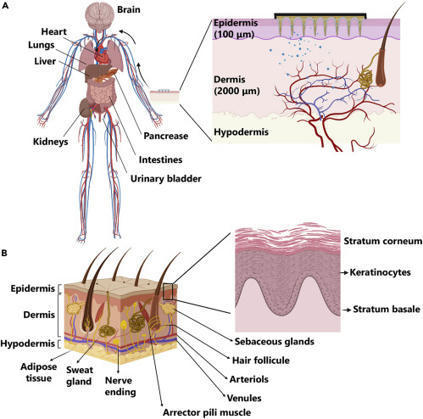
3D-printed microneedles in biomedical applications
www.cell.com
Nov. 21, 2022, 7:06 p.m.
Conventional needle technologies can be advanced with emerging nano- and micro-fabrication methods to fabricate microneedles. Nano-/micro-fabricated microneedles seek to mitigate penetration pain and tissue damage, as well as providing accurately controlled robust channels for administrating bioagents and collecting body fluids. Here, design and 3D printing strategies of microneedles are discussed with emerging applications in biomedical devices and healthcare technologies.
Share on

Tattoos can induce bloodstream infections
www.news-medical.net
Aug. 29, 2022, 9:12 a.m.
Tattooing is a painful process that involves the introduction of artificial pigment under the skin. If not performed hygienically, tattoos can induce various health complications, including immune and inflammatory reactions, infections, and chronic skin defects such as dermatoses. Between 2% and 27% of individuals experience some sort of discomfort after having a tattoo, with 0.5-6% developing skin infections.
Share on

Free webinar on microneedles for medical applications
www.nanoscribe.com
July 18, 2022, 10:31 a.m.
Live webinar on 3D Microfabrication of microneedles for medical applications using rapid prototyping and direct 3D printing for series production. Register now
Share on
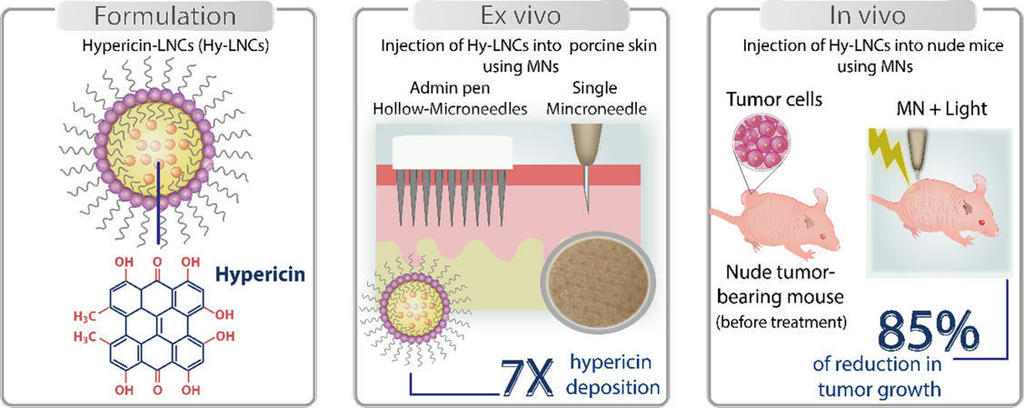
Hollow microneedle assisted intradermal delivery of hypericin lipid nanocapsules with light enabled photodynamic therapy against skin cancer
www.pharmaexcipients.com
July 3, 2022, 3:24 p.m.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) to manage non-melanoma skin cancers has garnered great attention over the past few years. Hypericin (Hy) is a potent lipid-soluble photosensitiser with promising anticancer therapeutic activities. Nevertheless, its poor water-solubility, aggregation in biological systems and insufficient skin penetration restricted its effective exploitation. Herein, we report for the first-time encapsulation of Hy into lipid nanocapsules (Hy-LNCs), and then application of an AdminPen™ hollow microneedles (Ho-MNs) array and an in-house fabricated Ho-MN to enable efficient intradermal delivery.
Share on