
US drops the number of vaccines it recommends for every child
www.wdef.com
Jan. 5, 2026, 9:04 p.m.
The change, which officials acknowledged was made without input from an advisory committee that typically consults on the vaccine schedule, came after President Donald Trump in December asked the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to review how peer nations approach vaccine recommendations and consider revising its guidance to align with theirs. HHS said its comparison to 20 peer nations found that the U.S. was an “outlier” in both the number of vaccinations and the number of doses it recommended to all children. Officials with the agency framed the change as a way to increase public trust by recommending only the most important vaccinations for children to receive.
Share on

Les États-Unis réduisent le nombre de vaccins recommandés pour chaque enfant
www.noovo.info
Jan. 5, 2026, 9:02 p.m.
Les États-Unis ont pris lundi une mesure sans précédent en réduisant le nombre de vaccins recommandés pour chaque enfant, laissant aux familles le choix d’autres vaccinations, telles que le vaccin contre la grippe, mais sans fournir de directives claires.
Share on

CDC flu data: Cases spike in 30 states as experts warn it’ll only get worse
www.independent.co.uk
Jan. 5, 2026, 8:59 p.m.
The A H3N2 flu virus, which historically caused the most hospitalizations and deaths in older people, is the most common strain in the US so far. Over 90% of analyzed H3N2 infections are a new subclade K variant, which differs from the strain in current flu vaccines. Flu seasons often don’t peak until January or February so health officials say it’s too early to know how big a problem the mismatch will be. The current flu season has already seen nine pediatric deaths, and emergency department visits for flu in children have exceeded last season's peak. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates at least 11 million illnesses, 120,000 hospitalizations, and 5,000 deaths from flu so far this season, recommending vaccination for everyone aged six months and older.
Share on

Covid-19 : tous les vaccinés invités à porter plainte pour tromperie sur les codages génétiques injectés –
www.nexus.fr
Jan. 6, 2024, 1:29 p.m.
Le 6 décembre dernier, une étude parue dans Nature a mis en évidence des erreurs de traduction de l’ARN messager modifié des vaccins anti-Covid. Ce dysfonctionnement a pour effet de produire un nombre indéterminé de protéines connues ou inconnues dans le corps, dont les effets pourraient être délétères. Suite à cette publication scientifique, l’avocat Jean-Pierre Joseph invite tous les vaccinés à porter plainte.
Share on
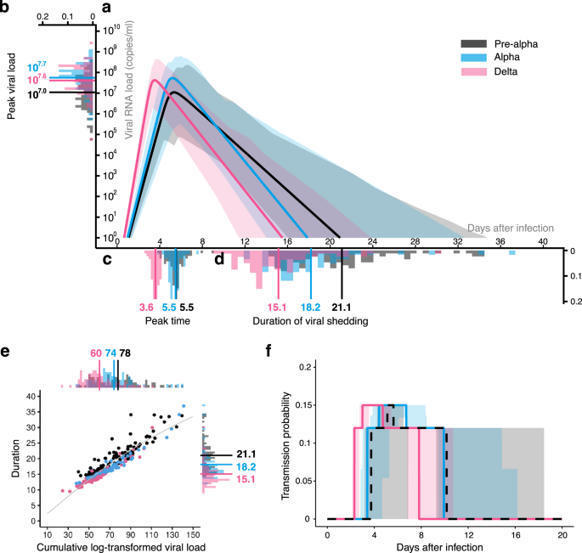
Isolation may select for earlier and higher peak viral load but shorter duration in SARS-CoV-2 evolution
www.nature.com
Nov. 26, 2023, 10:34 a.m.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, human behavior change as a result of nonpharmaceutical interventions such as isolation may have induced directional selection for viral evolution. By combining previously published empirical clinical data analysis and multi-level mathematical modeling, we find that the SARS-CoV-2 variants selected for as the virus evolved from the pre-Alpha to the Delta variant had earlier and higher peak in viral load dynamics but a shorter duration of infection. Selection for increased transmissibility shapes the viral load dynamics, and the isolation measure is likely to be a driver of these evolutionary transitions.
Share on

Specific HLA alleles may be associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection
www.news-medical.net
Nov. 26, 2023, 10:27 a.m.
The study analyzed the correlations between specific HLA alleles and the disease severity or T cell immune memory. The results showed that the alleles HLA-B*13:02 and -B*40:01 were associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may be due to their rare peptide anchors.
Share on

Safety of COVID-19 vaccines
www.ema.europa.eu
Nov. 26, 2023, 10:26 a.m.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) monitors the safety of COVID-19 vaccines authorised in the European Union (EU) extremely carefully. With hundreds of millions of people already vaccinated in the EU, this enables the continued detection of any rare side effects.
Share on
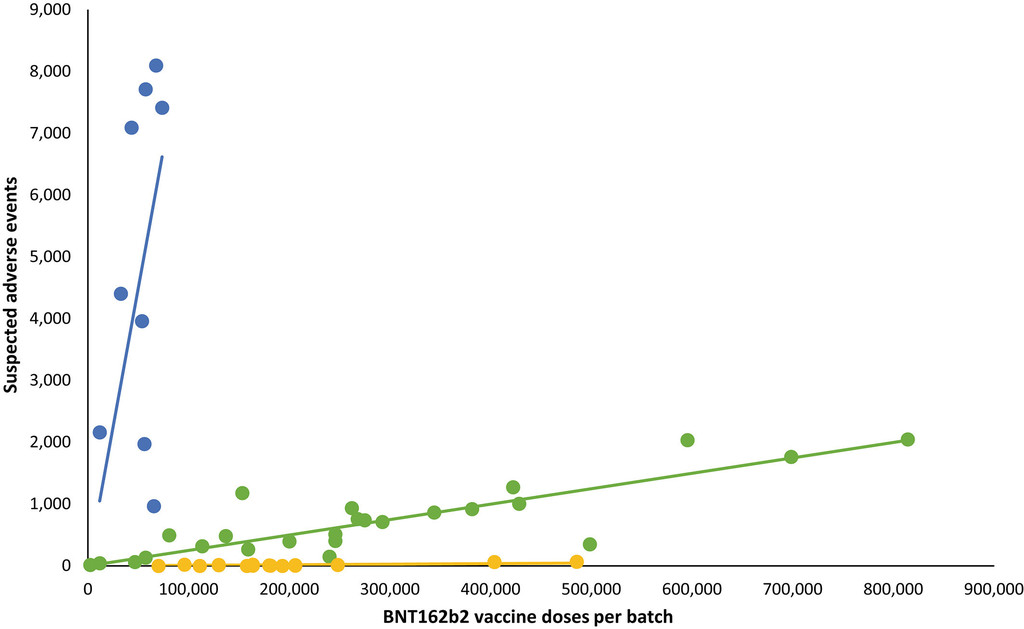
Batch‐dependent safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID‐19 vaccine
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Nov. 26, 2023, 10:17 a.m.
The results suggest the existence of a batch-dependent safety signal for the BNT162b2 vaccine, and more studies are warranted to explore this preliminary observation and its consequences.
Share on

Did lockdowns work? The verdict on Covid restrictions
iea.org.uk
July 22, 2023, 4:35 p.m.
COVID-19 lockdowns were “a global policy failure of gigantic proportions,” according to this peer-reviewed new academic study. The draconian policy failed to significantly reduce deaths while imposing substantial social, cultural, and economic costs.
Share on

Efficacy of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
June 22, 2023, 10:38 a.m.
This systematic review and meta-analysis showed that the use of hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine, with or without azithromycin, is not significantly associated with reductions in time to negative conversion of SARS-CoV-2 tests, length of stay, mortality, time to fever resolution, or incidence of mechanical ventilation compared with control groups based on very low quality of evidence. In addition, the use of hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine may not be associated with increased odds of adverse events, although this finding should be interpreted with caution as we observed a correlation between cumulative chloroquine base dose and the odds of adverse events, and the use of hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine was significantly associated with increased odds of adverse events when only studies with a low/moderate risk of bias was included in the analysis. Lastly, the use of hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine may be associated with increased odds of QT prolongations.
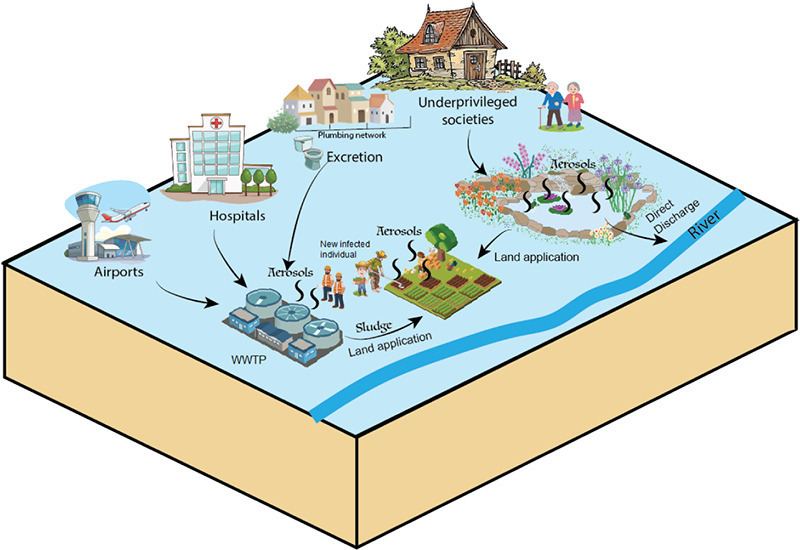
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via fecal-oral and aerosols–borne routes: Environmental dynamics and implications for wastewater management in underprivileged societies
www.sciencedirect.com
April 10, 2022, 6:48 p.m.
Although there is no current evidence showing that coronaviruses can be transmitted through contaminated drinking water, there is a growing concern on the impact of the current pandemic wave on underprivileged societies because of their poor wastewater treatment infrastructures, overpopulation, and outbreak management strategies. More research is encouraged to trace the actual fate of SARS-CoV-2 in the environment and to develop/revise the disinfection strategies accordingly.
Share on
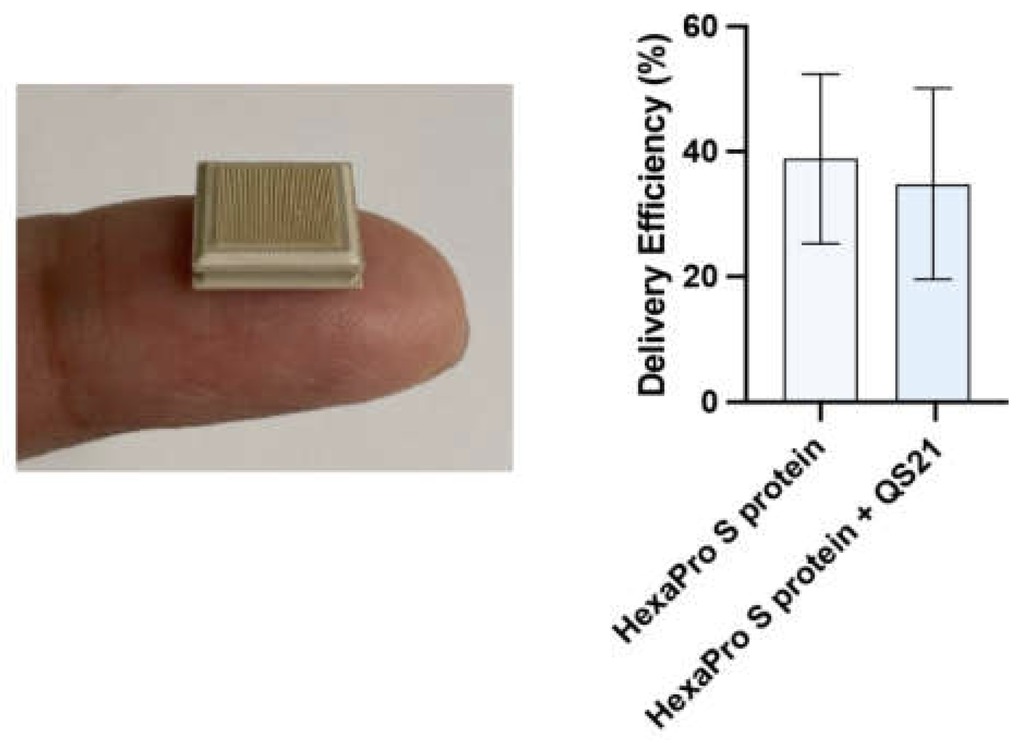
Dermal Delivery of a SARS-CoV-2 Subunit Vaccine Induces Immunogenicity against Variants of Concern
www.mdpi.com
April 10, 2022, 6:45 p.m.
In this study, a modified, HexaPro S protein subunit vaccine, delivered using a needle-free high-density microarray patch (HD-MAP), was investigated for its immunogenicity and virus-neutralizing abilities. Mice given two doses of the vaccine candidate generated potent antibody responses capable of neutralizing the parental SARS-CoV-2 virus as well as the variants of concern, Alpha and Delta. These results demonstrate that this alternative vaccination strategy has the potential to mitigate the effect of emerging viral variants.
Share on
Study finds higher risk of thrombotic events after SARS-CoV-2 infection
www.news-medical.net
April 10, 2022, 6:41 p.m.
A study from Sweden published by The BMJ today finds an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (a blood clot in the leg) up to three months after covid-19 infection, pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung) up to six months, and a bleeding event up to two months. The findings also show a higher risk of events in patients with underlying conditions (comorbidities), patients with more severe covid-19, and during the first pandemic wave compared with the second and third waves.
Share on

Plenty of Evidence for Recombination in SARS-CoV-2
www.the-scientist.com
April 10, 2022, 6:40 p.m.
Recombination—the exchange of genetic material between genomes—is common in coronaviruses because of the way they copy their RNA genomes. During replication, the RNA-synthesizing enzyme these viruses use duplicates shorter sections close to the end of the genome in addition to making the long template it needs for generating whole-genome copies. Furthermore, the enzyme is prone to switching from one template to another, so if a cell has multiple viral genomes in it, the enzyme may stitch together bits from different viruses to create a kind of Frankenstein genome.
Share on
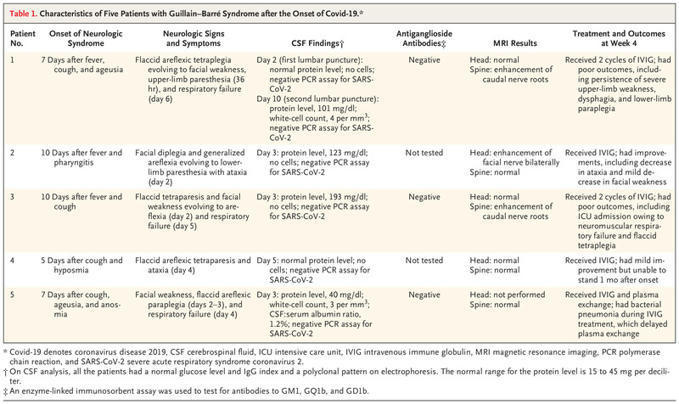
Guillain–Barré Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2
www.nejm.org
April 10, 2022, 6:39 p.m.
On the basis of this observational series involving five patients, it is not possible to determine whether severe deficits and axonal involvement are typical features of Covid-19–associated Guillain–Barré syndrome. We could not determine the effect of reduced vital capacity due to neuromuscular failure from Guillain–Barré syndrome in these patients, but such an effect might be considered if findings on chest imaging are not commensurate with the severity of respiratory insufficiency. Guillain–Barré syndrome with Covid-19 should be distinguished from critical illness neuropathy and myopathy, which tend to appear later in the course of critical illness than Guillain–Barré syndrome.
Share on
SARS-CoV-2 detected using smartphone biosensor
www.news-medical.net
April 10, 2022, 6:38 p.m.
Although the majority of individuals who are infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will remain asymptomatic, they are still capable of transmitting the virus the others. In addition to the widespread prevalence of asymptomatic carriers, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can also be difficult to diagnose, as those who are asymptomatic often experience symptoms similar to both the flu and pneumonia.
Share on
Role of natural immunity to SARS-CoV-2 on post-vaccination antibody responses in staff and residents of long-term care facilities
www.news-medical.net
April 10, 2022, 6:38 p.m.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that has led to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has caused 400 million infections throughout the world, with 78 million infections in the United States (US) alone. Two million of those infections are reported in staff and residents of long-term care facilities (LTCFs). They represent around 16% of total deaths in the US.
Share on
SARS-CoV-2 mutations capable of widespread T-cell escape
www.news-medical.net
April 10, 2022, 6:38 p.m.
Both natural infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and immunization against this virus can generate SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies and T-cells. However, the level of immunity provided by these methods is challenged by the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, which has led to the emergence of new genetic variants like the Omicron variant.
Share on

SARS-CoV-2 mutations capable of widespread T-cell escape
www.news-medical.net
April 10, 2022, 6:37 p.m.
Both natural infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and immunization against this virus can generate SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies and T-cells. However, the level of immunity provided by these methods is challenged by the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, which has led to the emergence of new genetic variants like the Omicron variant.
Share on
A massive study finds diabetes risk rises after COVID-19
interestingengineering.com
April 2, 2022, 3:25 p.m.
The researchers saw that the risk of developing diabetes rose as COVID-19 severity increased. When compared to people who did not have COVID-19 and were not hospitalized or admitted to intensive care, those who were hospitalized or admitted to intensive care had roughly four times the risk.
Share on