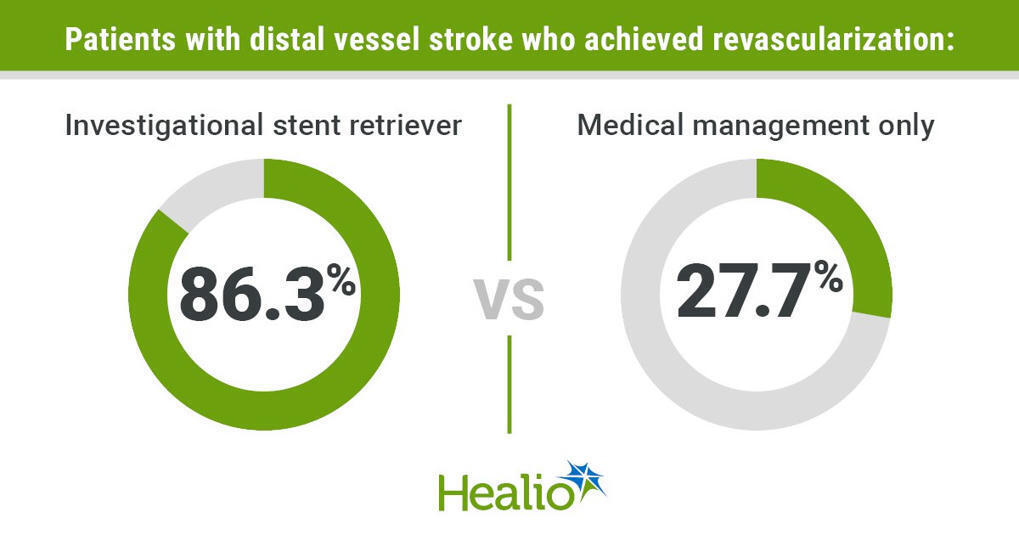
Device restores blood flow in distal stroke
www.healio.com
Feb. 23, 2026, 9:06 a.m.
An investigational stent retriever device was highly effective in restoring blood flow in distal vessel ischemic stroke.Data on key secondary efficacy and safety endpoints will be presented at a later date.
Share on
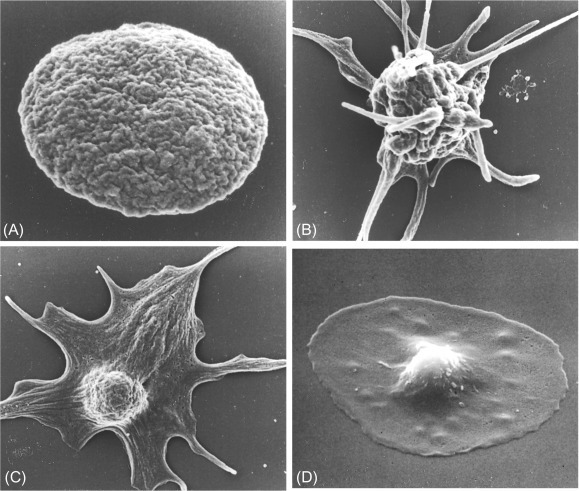
The Structure of Resting and Activated Platelets
www.sciencedirect.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 11:01 a.m.
At first glance, the platelet is a simple cell. However, its small size hides an extremely well conserved structure that is vital for its function in both hemostasis and vascular integrity and development. A combination of electron microscopy, light microscopy, biochemical, and cell biology studies has, over the years, revealed this structure to us and allowed the important functions of the various organelles and subcellular components to be understood. This chapter reviews the structure of the resting platelet and discusses the dramatic and dynamic changes, especially in the cytoskeleton, that occur upon activation to allow platelets to carry out their primary function in hemostasis.
Share on
Post-thrombectomy alteplase linked to better stroke outcomes
www.news-medical.net
Feb. 9, 2026, 1:35 p.m.
Large-artery ischemic (clot-caused) strokes account for about 1 in 4 ischemic strokes, according to study author ángel Chamorro, M.D., Ph.D., professor of neurology at the University of Barcelona and head of the Comprehensive Stroke Center Hospital Clinic in Barcelona. These types of strokes can cause death and long-term disability because they block large arteries that supply blood to significant areas of the brain.
Share on

Société des Neurosciences • Expérimentation animale
www.neurosciences.asso.fr
Feb. 7, 2026, 10:06 a.m.
Initiée par le Ministère de la Recherche de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de l’Innovation, cette démarche est coordonnée par le Gircor, et fait écho à des initiatives similaires dans d’autres pays européens. En tant que signataire de cette Charte de transparence, la Société des Neurosciences s’engage à mieux informer le grand public sur l’utilisation d’animaux dans la recherche scientifique française en neurosciences.
Share on
Naox nabs 1st FDA clearance for in-ear EEG device
www.fiercebiotech.com
Feb. 4, 2026, 2:12 p.m.
Naox Technologies has become the first medtech company to receive FDA clearance for its in-ear EEG device that can negate the need for complex and limited scalp electrodes that have been used for brain monitoring for decades.Naox Link is an electroencephalography (EEG) platform that patients use via a small sensor worn in the ear, allowing brain activity to be monitored while they move around. According to a Jan. 6 release, the approach “enables long-duration, real-world brain monitoring beyond traditional hospital environments.”
Share on

New Guidance on Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke
www.medscape.com
Feb. 2, 2026, 9:44 a.m.
Stroke is now the fourth leading cause of death in the US, with one person dying about every 3 minutes, according to the latest statistics. Over the past decade, several landmark trials have reshaped acute stroke care, including interventions for large vessel occlusion, thrombolysis, or endovascular thrombectomy (EVT), and streamlined hospital workflows.“The 2026 guidance brings that progress together to standardize stroke care across hospitals of all sizes and ensure rapid, evidence-based treatment for every patient, regardless of where they live,” the AHA/ASA noted.
Share on

Sino Medical Sciences Technology's AUCURA Flow-Diverting Stent Approved by NMPA
flcube.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 2:20 p.m.
China-based Sino Medical Sciences Technology Inc. (SHA: 688108) announced that its holding subsidiary Neurovita has received market approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for its AUCURA flow-diverting stent. This approval is for the treatment of adult patients with ruptured cystic or fusiform wide neck aneurysms (neck width ≥ 4mm or tumor/neck ratio < 2) of the internal carotid artery (from the petrous segment to the distal end) and vertebral artery, with a diameter of the tumor-carrying vessel ranging from 2.0mm to 6.0mm.
Share on

Endovascular treatment of symptomatic severe intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis with a novel intracranial dedicated drug-eluting stent
www.frontiersin.org
Jan. 26, 2026, 2:14 p.m.
This study indicated a favorable midterm clinical outcome of the novel intracranial DES NOVA stent, with a low rate of ISR and without increasing the incidence of periprocedural complications in highly selected patients. The NOVA stent represents a promising new therapy to treat ICAS. However, the clinical results need to be further verified by larger sample size controlled studies with longer follow-up periods.
Share on
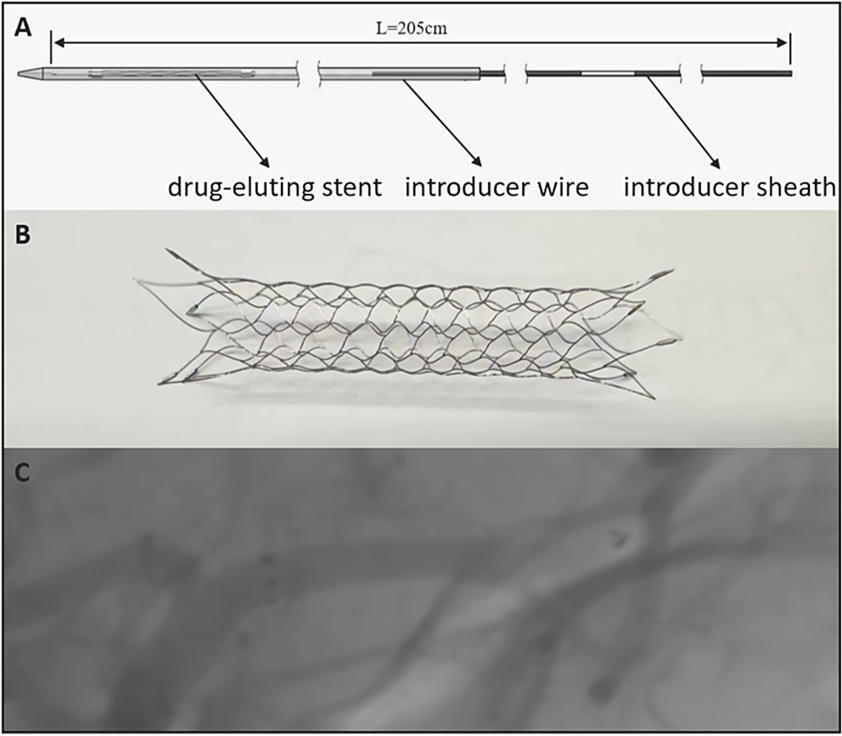
Self-expanding intracranial drug-eluting stent system in patients with symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: initial experience and midterm angiographic follow-up
link.springer.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 2:07 p.m.
COMETIU is safe and effective for treating ICAS, with minimal risk during the procedure and a low rate of ISR during medium-term follow-up.
Share on

Simple Blood Test Predicts Stroke Outcomes
www.medscape.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:29 a.m.
In patients with acute ischaemic stroke receiving reperfusion therapies such as mechanical thrombectomy (MT) or intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), an elevated neutrophil‑to‑lymphocyte ratio before treatment was associated with poor functional outcomes, whereas a higher lymphocyte‑to‑monocyte ratio was linked to better functional outcomes after MT.
Share on

Machine learning for predicting functional outcomes in acute ischemic stroke: insights from a nationwide stroke registry
www.nature.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:28 a.m.
Accurately predicting the prognosis of patients with acute ischemic stroke at discharge remains highly challenging after active treatment. The aim of this retrospective nationwide registry-based study was to identify key predictors associated with favorable outcomes and to develop machine learning models for patient outcome prediction.
Share on

Thromboinflammation dans l’accident vasculaire cérébral ischémique - Vers de nouvelles opportunités thérapeutiques ? | médecine/sciences
www.medecinesciences.org
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:27 a.m.
L’accident vasculaire cérébral ischémique résulte de l’occlusion d’une artère intracrânienne, et son traitement nécessite une recanalisation artérielle rapide afin de rétablir la perfusion cérébrale. Les traitements actuels de recanalisation artérielle, la thrombolyse intraveineuse et la thrombectomie mécanique, ont amélioré le pronostic, mais leur faisabilité est restreinte et leur capacité à rétablir une bonne reperfusion cérébrale reste limitée. Des expériences dans des modèles animaux d’accident vasculaire cérébral ischémique, ainsi que des données cliniques, suggèrent que la thromboinflammation serait un facteur clé de résistance à ces traitements, non seulement en limitant l’efficacité de la thrombolyse intraveineuse, mais également en découplant recanalisation artérielle et reperfusion cérébrale.
Share on
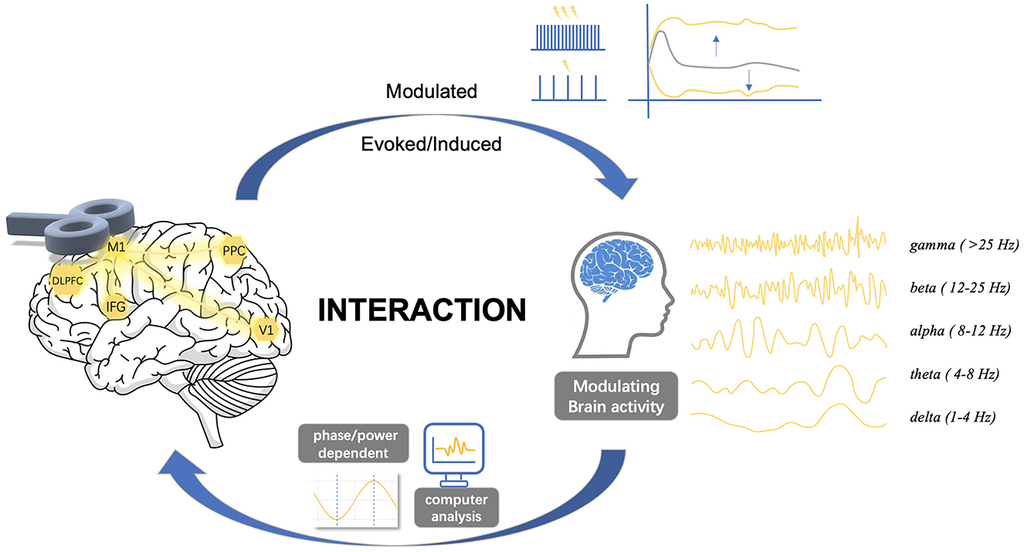
Improving of Brain-Machine Interaction Performance by Sensory and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
link.springer.com
Jan. 19, 2026, 11:36 a.m.
In this study, we address the issue of whether applying transcranial magnetic and vibrotactile stimulation can improve the motor imagery BMI performance. Our findings provide evidence that applying transcranial magnetic stimulation with specified parameters (frequency 5 Hz, duration 6 min, 90% of the muscle activation threshold at rest) leads to preactivation of the occipital brain region and facilitates sensorimotor integration during motor imagery. We found that this process results in TMS-induced decrease of the motor imagery BMI latency. Integration of vibrotactile feedback in motor imagery BMI leads to enhancement of the BMI performance by an increase of the ERD level of EEG patterns over the contralateral motor cortex area corresponding to the MI of the non-dominant hand and an increase in motor cortical excitability.
Share on

Nitinol Stent Placement in a Stenosed Artery: A Highly Nonlinear Application Scenario for Two Novel Finite-Element Models
link.springer.com
Dec. 29, 2025, 7:15 p.m.
To capture the damage in the artery induced by the stent, a gradient-enhanced damage model for arteries is implemented. It allows a detailed investigation of damage onset and evolution and proves to be numerically robust. Due to the modularity of the damage model, further characteristics of the artery such as prestretch, anisotropic behavior, and mass turnover can be readily incorporated.
Share on
Scientists found a way to restore brain blood flow in dementia
www.sciencedaily.com
Dec. 25, 2025, 2:04 p.m.
A new study suggests that dementia may be driven in part by faulty blood flow in the brain. Researchers found that losing a key lipid causes blood vessels to become overactive, disrupting circulation and starving brain tissue. When the missing molecule was restored, normal blood flow returned. This discovery opens the door to new treatments aimed at fixing vascular problems in dementia.
Share on

Mumbai doctors observing rise in brain stroke cases during the winter
www.mid-day.com
Dec. 15, 2025, 10:47 a.m.
The factors causing a surge in stroke cases during winter are a cold-induced rise in blood pressure, dehydration, and reduced activity. Experts emphasise awareness and preventive measures to protect at-risk individuals
Share on
Study Shows How AI is Transforming Stroke Care
www.dicardiology.com
Dec. 8, 2025, 9:28 a.m.
Study in Lancet Digital Health represents the largest real-world evaluation of stroke AI imaging, encompassing data from more than 450,000 patients admitted to more than 100 NHS England hospitals over a 5-year period
Share on

CREST-2 Study Highlights Benefits of Carotid Artery Stenting
www.dicardiology.com
Nov. 30, 2025, 10:13 p.m.
According to a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, carotid artery stenting combined with medical therapy demonstrated a significantly lower stroke risk compared to intensive medical therapy alone in patients with severe asymptomatic carotid stenosis.
Share on
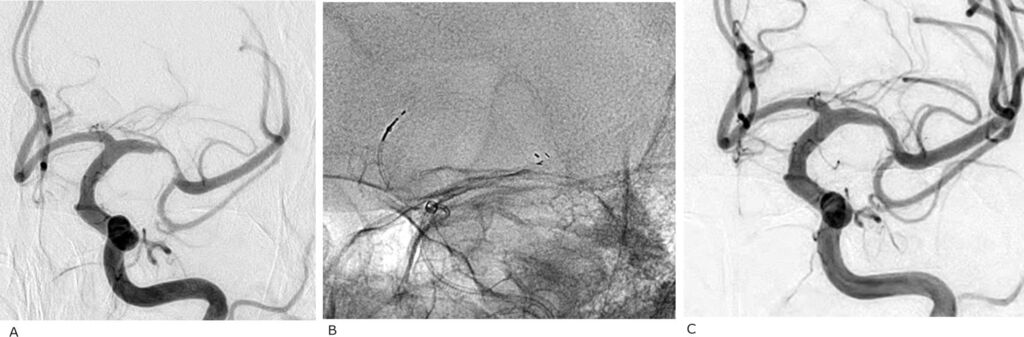
First-in-human trial of a self-expandable, temporary dilation system for intracranial atherosclerotic disease in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke
jnis.bmj.com
Nov. 30, 2025, 9:30 p.m.
Intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD) significantly contributes to ischemic stroke, especially among Asian populations. Large vessel occlusion (LVO) due to underlying ICAD accounts for 15–35% of acute ischemic stroke cases requiring endovascular therapy. However, the successful recanalization rate of ICAD-related LVO remains lower. The TG dilator is a self-expandable device, temporarily dilating ICAD-related blocked blood vessels.
Share on
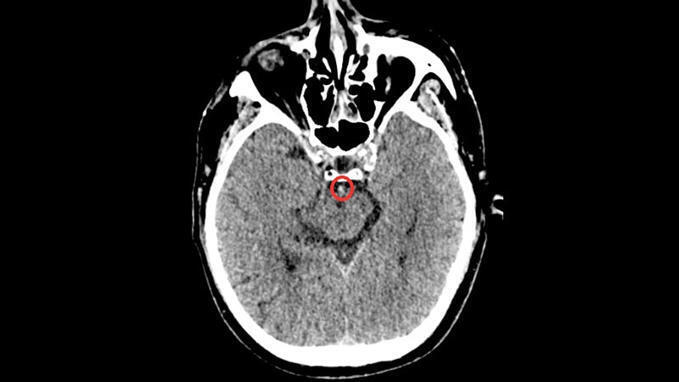
Thrombectomy Choice in Basilar Stroke May Hinge on Clot Type
www.medscape.com
Nov. 30, 2025, 3:34 p.m.
In stroke due to basilar artery occlusion, the best technique to use for thrombectomy appears to depend on the underlying etiology of the clot, a new trial suggested. The Chinese ANGEL-COAST randomized trial compared two different techniques used for endovascular thrombectomy — either contact aspiration or stent retriever — in patients with basilar artery occlusion stroke. Results showed that using contact aspiration on the first attempt at clot removal achieved higher initial reperfusion rates without increasing the risk for symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage or periprocedural complications.
Share on