
Incidence and costs of bleeding-related complications in French hospitals following surgery for various diagnoses
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
June 24, 2025, 8:32 a.m.
This study estimated increases of hospital LOS and costs for patients with severe surgical bleeding complications in France. Hospitalisations longer than the average LOS across all DRGs indicated significant costs associated with severe post-surgical bleeding. Awareness of the clinical and economic consequences of severe post-surgical bleeding provides an important framework when evaluating blood conservation strategies.
Share on
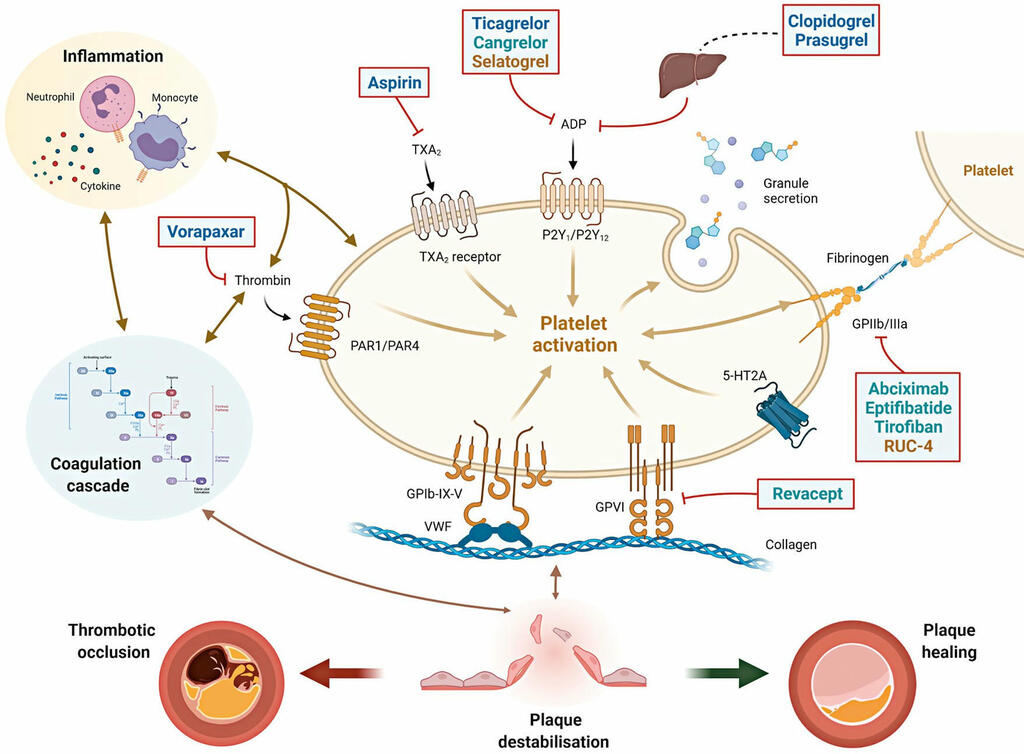
Antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention
eurointervention.pcronline.com
June 24, 2025, 8:03 a.m.
Antiplatelet therapy is key to reducing local thrombotic complications and systemic ischaemic events among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI), but it is inevitably associated with increased bleeding. The continuous refinement in stent technologies, together with the high incidence of ischaemic recurrences after PCI and the understanding of prognostic implications associated with bleeding, have led to a substantial evolution in antiplatelet treatment regimens over the past decades.
Share on
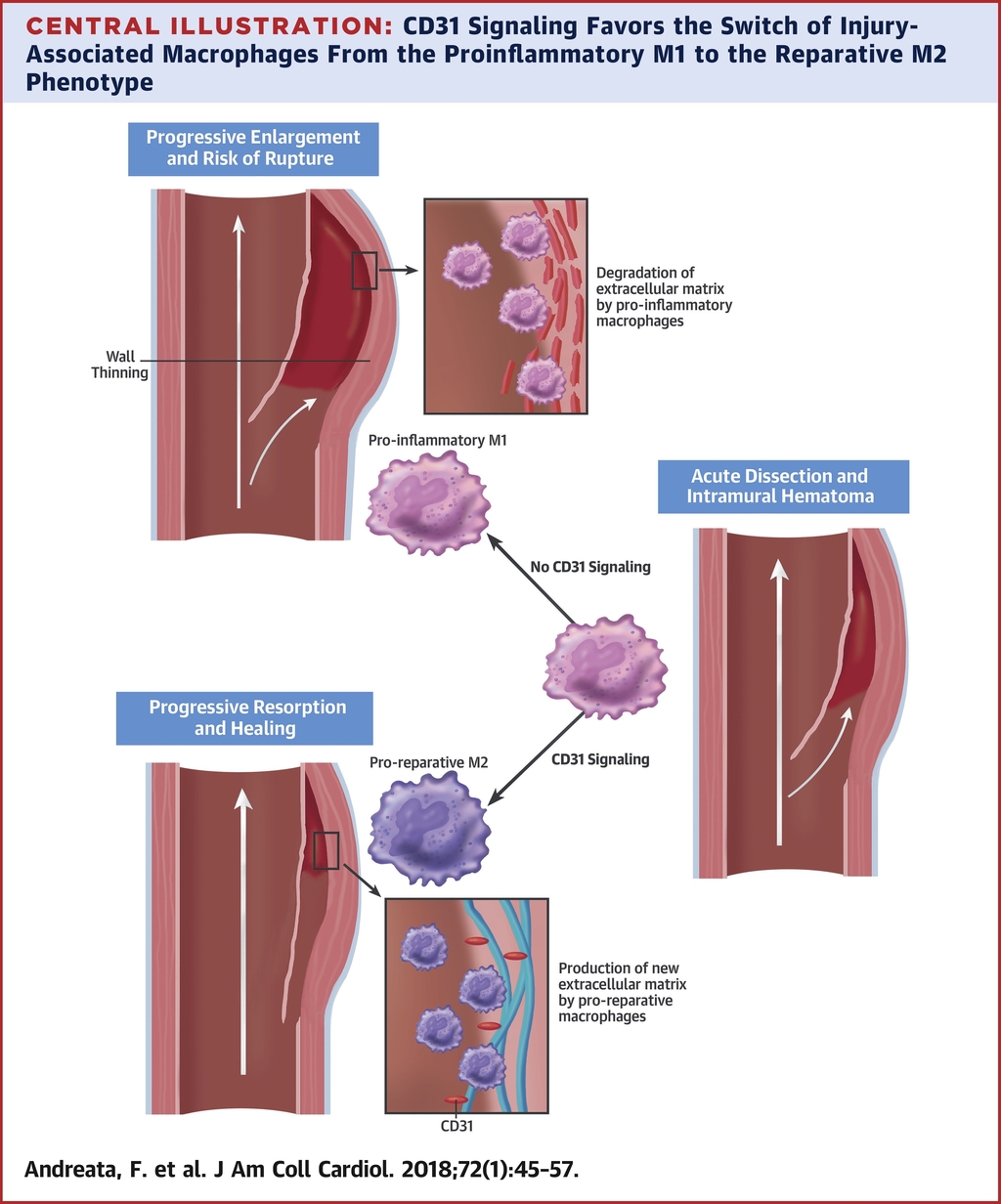
Macrophage CD31 Signaling in Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm
www.jacc.org
June 18, 2025, 1 p.m.
CD31 signaling promotes the switching of proinflammatory macrophages to the reparative phenotype and favors the healing of experimental dissected aortas. Treatment with a drug-suitable CD31 agonist may facilitate the clinical management of ADIM.
Share on
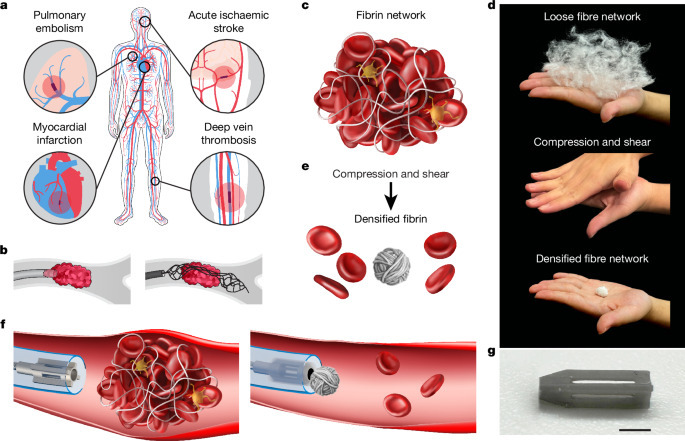
Milli-spinner thrombectomy
www.nature.com
June 14, 2025, 12:39 p.m.
Clot-induced blockage in arteries or veins can cause severe medical conditions. Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive technique used to treat ischaemic stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism and peripheral vascular disease by removing clots through aspiration, stent retriever or cutting mechanisms. However, current mechanical thrombectomy methods fail to remove clots in 10–30% of patients, especially in the case of large, fibrin-rich clots. These methods can also rupture and fragment clots, causing distal emboli and poor outcomes. To overcome these challenges, we develop the milli-spinner thrombectomy, which uses a simple yet innovative mechanics concept to modify the clot’s microstructure, facilitating its removal.
Share on

Neuroangiogenesis potential of mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles in ischemic stroke conditions
biosignaling.biomedcentral.com
June 9, 2025, 6:19 a.m.
In past decades, the discovery of stem cells and byproducts has led to promising results in in vitro settings and pre-clinical studies. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nano-sized particles released from various cell types, for instance, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), with certain signaling biomolecules, growth factors, and cytokines involved in cell-to-cell communication. A great plethora of studies have pointed to the fact that EVs with specific cargo can distribute easily in different parts of the body, making them appropriate therapeutics under different pathological conditions. The current review articles aimed to highlight the neuroangiogenesis properties of MSC EVs in IS conditions. How and by which mechanisms MSC EVs can orchestrate the process of nervous system regeneration is at the center of debate.
Share on

Sino Medical Sciences Technology's AUCURA Flow-Diverting Stent Approved by NMPA
flcube.com
May 30, 2025, 10:51 a.m.
AUCURA represents China’s first flow-diverting stent featuring both 0.017-inch system deliverability and an antithrombotic coating. The stent is woven from cobalt-chromium-platinum DFT wire with full-body radiopacity. Its superhydrophilic surface technology reduces contact angle to minimize plasma protein/platelet adhesion, significantly lowering the risk of stent thrombosis. By modifying aneurysm hemodynamics and promoting endothelial healing at the neck region, AUCURA enables effective treatment of intracranial aneurysms.

NeuroVita's AUCURA™ Novel eG Coated Flow-Diverter receives NMPA approval
mp.weixin.qq.com
May 30, 2025, 10:42 a.m.
The AUCURA blood flow-diverter was officially approved by China's National Drug Administration (NMPA). This product is the first dense-mesh stent that can be transported by a 0.017" system, and with an antithrombotic eG NTMA coating, bringing a complete upgrade in the treatment of intracranial aneurysm.
Share on

Artedrone tries robots and magnets for autonomous thrombectomy
www.medicaldesignandoutsourcing.com
May 26, 2025, 11:05 a.m.
Expanding care to stroke victims is one of medtech’s biggest opportunities, and startup Artedrone is developing a microrobot system that can navigate to blood clots for autonomous mechanical thrombectomies.
Share on
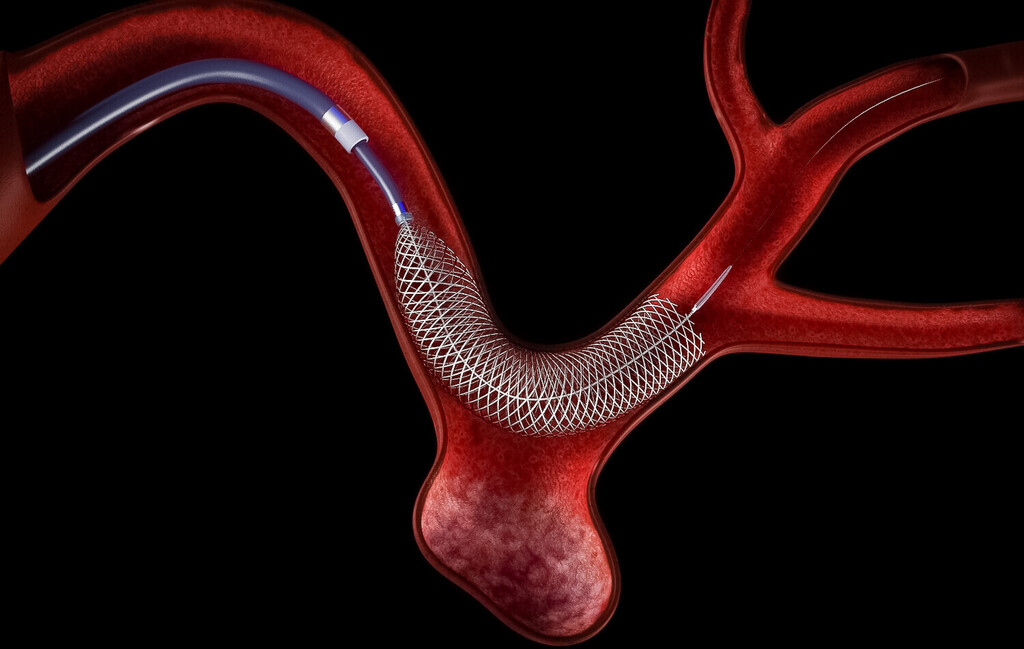
Heparin Coating Decreases the Thrombotic Signature of Flow Diverter Stents
link.springer.com
April 21, 2025, 11:45 a.m.
The findings demonstrate that heparin coated flow diverter stents are characterized by a lower thrombotic signature than bare metal flow diverter stents and raise the possibility of an additional therapeutic option to treat intracranial aneurysms.
Share on

Comparison of the hemocompatibility of neurovascular flow diverters with anti-thrombogenic coatings
www.sciencedirect.com
April 21, 2025, 11:42 a.m.
Despite the continual progress in technology, thromboembolic complications still occur following endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms and remain the primary contributor to morbidity and mortality. Thus, coating the surfaces of blood-contacting flow diverters may reduce thrombus-related complications in clinical use. In this study, the hemocompatibility of different commercially available flow diverters Pipeline Flex Embolization Device with Shield Technology (Medtronic), the p64 MW HPC (Phenox), and the DERIVO 2heal (Acandis) was investigated using an in vitro blood circulation model.
Share on

Endovascular brain procedures: The next frontier for vascular surgery?
vascularnews.com
April 20, 2025, 8:57 a.m.
While stroke treatment has dramatically changed in recent years, still around 795,000 people experience a new or recurrent stroke each year, and of all strokes 87% are ischaemic.1 A high variability in accessing stroke treatments exists across different countries or different regions within the same nation, even if at present guidelines are quite definitive in indicating endovenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy (MT) in selected cases as key treatment points. However, treatment indications are continuously evolving and so the vascular surgery world should be prepared to evolve accordingly.
Share on

Inari Medical, now part of Stryker, launches Artix thrombectomy system
vascularnews.com
April 20, 2025, 8:42 a.m.
Stryker notes that the Artix system builds on the success of Inari’s venous thrombectomy devices and is its inaugural entry into the arterial space. “Inari offers a comprehensive toolkit approach to arterial thrombectomy with an innovative, over-the-wire system that provides physicians with the flexibility to aspirate and/or mechanically extract a clot,” a press release reads.
Share on

Working Status in Patients With Untreated Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
www.neurosurgery-blog.com
April 19, 2025, 4:28 p.m.
The study assessed the working status of Norwegian patients with untreated unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) from 2008 to 2018. It found that these patients had significantly lower work participation pre- and post-diagnosis compared to the general population, highlighting potential psychological and health burdens.
Share on
Age-Adjusted Ischemic Stroke Mortality Increased Since 2009
www.drugs.com
April 19, 2025, 4:03 p.m.
The researchers found that across all urbanization levels, the age-adjusted ischemic stroke mortality rates increased since 2009; the most pronounced increases were seen in nonmetropolitan areas. There was an increasing proportion of deaths at home, shifting from inpatient medical facilities. There were significant disparities in access to specialized end-of-life stroke care, especially for racial minorities and rural residents. The likelihood of dying in less specialized environments was increased for Black/African American individuals and those in rural settings due to health care access barriers.
Share on

Another Medtronic recall - 17 injuries, 4 deaths.
mp.weixin.qq.com
March 31, 2025, 5:59 p.m.
Medtronic's Pipeline Vantage embolization device with Shield Technology is used to treat cerebral aneurysms. This endovascular interventional device is implanted into a blood vessel through a minimally invasive catheter to deliver the braided catheter to the aneurysm site to block blood flow.
Share on

Rivaroxaban shown to be a viable alternative to warfarin for left ventricular thrombus
www.news-medical.net
March 31, 2025, 9:10 a.m.
Warfarin is the standard treatment for left ventricular thrombus. However, patients taking warfarin must undergo frequent blood tests to check that the time it takes for their blood to clot remains in a therapeutic range (an INR, International Normalized Ratio, of 2-3). Many other medications and foods can interact with warfarin, potentially increasing the patient's risk for ischemic and bleeding complications.
Share on

Chinese Expert Consensus on the Treatment of Cranial Aneurysms with Blood Flow Guided Devices
mp.weixin.qq.com
March 23, 2025, 4:30 p.m.
The intracranial aneurysm has a certain incidence in the general population, the fatality rate is high after rupture, and the safety and effectiveness of intravascular therapy have been confirmed by many trials, but the intravascular treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms is still facing challenges. The blood flow guidance device (FD) developed based on the hemodynamic research of intracranial aneurysm, changed the concept of intravascular treatment, and its principle is to reshape the local blood flow so that the aneurysm forms thrombosis in the aneurysm and thus block the aneurysm. However, the large-scale application of FD in clinical time is short, and its indications, perioperative period management, surgical operation techniques, and complication prevention and treatment are clinically controversial, and there are no relevant guidelines or consensus in China.
Share on

Worrying amounts of microplastics found in human brain tissue - how to reduce exposure
www.universal-sci.com
March 4, 2025, 3:26 p.m.
Microplastics are everywhere—in our water, food, and even the air we breathe. A new scientific review highlights a growing concern: microplastics and nanoplastics are accumulating in human brain tissue. Researchers are now investigating what this could mean for brain health and how we can reduce our exposure.
Share on

Robeauté raises $28 million for neurosurgical microrobots to transform brain health
med-techinsights.com
March 4, 2025, 3:22 p.m.
Robeauté, the medtech startup developing neurosurgical microrobots, is announcing it has raised 28 million USD led by Plural, Cherry Ventures and Kindred Ventures. Other investors including LocalGlobe, Think.Health and previous investors APEX Ventures participated, along with strategic investment from Brainlab. The new funding will be used to continue developing the technology, starting human trials in 2026 and setting up US operations ahead of FDA approval and full go-to-market.
Share on

Boston Scientific snags Silk Road Medical in $1.26B deal
www.fiercebiotech.com
March 4, 2025, 3:18 p.m.
Silk Road is known as the developer of TCAR, for transcarotid artery revascularization. In patients that need a stent to help clear a path through a plaque-filled vessel, the company’s Enroute hardware temporarily reverses the flow of blood, to redirect any potentially dangerous loose clots away from the brain.
Share on