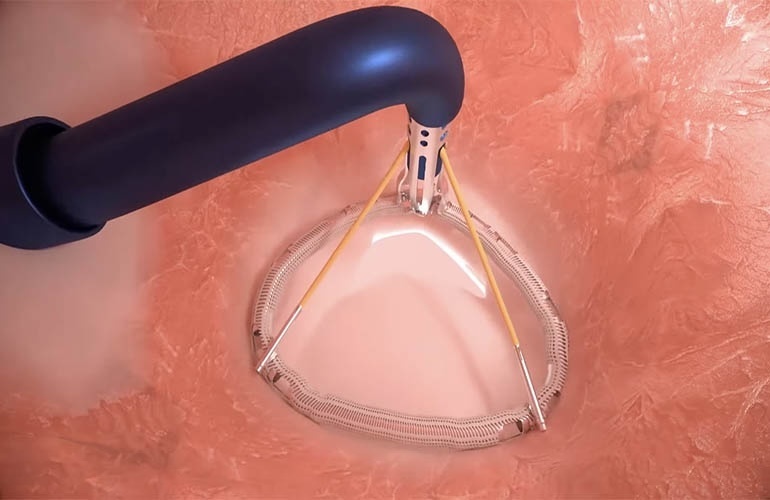
Valcare Medical Announces First U.S. Transseptal AMEND™ Implant in Early Feasibility Study
www.prnewswire.com
Feb. 16, 2026, 9:54 a.m.
The AMEND™ System delivers a closed, D-shaped, semi-rigid annuloplasty ring through catheter in a transseptal approach. It is specifically designed to mimic the anatomical remodeling and clinical results achieved by traditional surgical annuloplasty—the technique used in most open-heart mitral valve repairs. Unlike other transcatheter mitral repair technologies, the AMEND System is designed to preserve future treatment options if clinically required later.
Share on

Transseptal TMVR system gains US FDA approval
cardiovascularnews.com
Dec. 29, 2025, 12:58 p.m.
The Sapien M3 transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) system is indicated for the treatment of symptomatic moderate-to-severe or severe MR in patients who are deemed unsuitable for surgery or transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) therapy by a multidisciplinary heart team.
Share on

What Is the Average Age for Heart Valve Replacement?
blog.regimenhealthcare.com
Dec. 29, 2025, 12:58 p.m.
Heart valve replacement is a common cardiac procedure, but many patients and families ask one key question: what is the average age for heart valve replacement?In most cases, heart valve replacement is performed between 60 and 75 years of age, although the exact age varies depending on the valve involved, the underlying heart condition, and the patient’s overall health.
Share on

Philips, Edwards team on AI-based guide for mitral valve repair
www.medtechdive.com
Dec. 6, 2025, 12:40 p.m.
Artificial intelligence combines ultrasound and X-ray images to give physicians a real-time 3D view of the repair device during transcatheter heart procedures.
Share on

Latest data from Dragonfly pivotal studies shared at PCR London Valves
cardiovascularnews.com
Dec. 6, 2025, 12:39 p.m.
The device, which can be deployed for transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) in the mitral or tricuspid valves, has similar design features to existing mitral TEER devices including MitraClip (Abbott) and Pascal (Edwards Lifesciences), and includes a mechanical closure system and central spacer. The device has received approval from China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and CE mark to date.
Share on

“Durable” valve performance seen with early generation transapical TMVR system
cardiovascularnews.com
Dec. 6, 2025, 12:38 p.m.
The study, which began enrolling in 2015, charts early use of the Intrepid device featuring a transapical delivery system, though later generations of the device have switched to using a transfemoral approach. Procedures were conducted at 21 sites spanning Europe, Australia and the USA and involved 95 patients with symptomatic severe MR who were at high risk for surgery.
Share on

AltaValve early feasibility study reports out to one year
cardiovascularnews.com
Dec. 6, 2025, 12:38 p.m.
Left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction is a common limitation of existing TMVR technologies leading to high rates of screen failure for patients screened for TMVR trials, Ninios highlighted in his presentation, ranking this alongside mitral annulus size and the presence of mitral annular calcification (MAC) as the exclusions that comprise the “Achilles’ heel” of existing TMVR technologies. AltaValve System’s atrial fixation TMVR device is designed to minimise the risk of LVOT obstruction and treat a broad population of mitral regurgitation (MR) patients as well as varied mitral annulus sizes.
Share on

Clinical Outcomes and In-hospital Mortality Rate following Heart Valve Replacements at a Tertiary-care Hospital
xiahepublishing.com
Nov. 30, 2025, 9:14 p.m.
Over the past five years, we observed a 7.24% mortality rate at our tertiary care facility following prosthetic heart valve implantation across all age groups. The data suggest that mortality may be more common among females and older individuals; however, these differences did not reach statistical significance.
Share on

Less-Invasive Valve Replacement Changing Patients’ Lives
www.medscape.com
Nov. 24, 2025, 10:53 a.m.
Minimally invasive cardiac procedures such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), catheter-based mitral valve repair, and percutaneous atrial septal defect closure fail at times to attract the same attention given to traditional open-heart surgeries, particularly high-profile procedures such as a coronary artery bypass graft. Studies like this one from the March 2021 issue of the Journal of Thoracic Disease discuss the debate over outcomes, quality, and safety that has followed these procedures.
Share on

Transseptal TMVR system shows promise in patients unsuited for surgery or TEER
cardiovascularnews.com
Nov. 17, 2025, 2:07 p.m.
Results of a pivotal clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a fully percutaneous transseptal mitral valve replacement (TMVR) procedure—Sapien M3 (Edwards Lifesciences)—in patients with symptomatic, moderate-to-severe mitral regurgitation (MR) who are not eligible for surgery or mitral-transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) procedures, demonstrated effective MR reduction with low rates of complications and mortality.
Share on
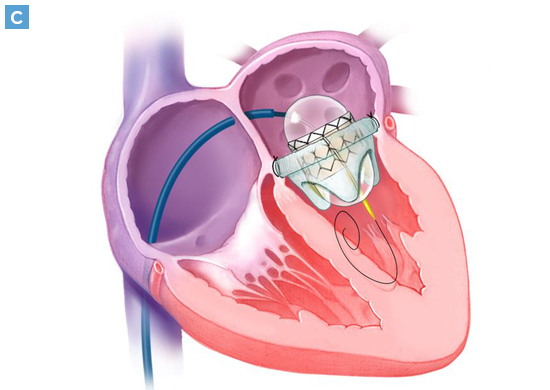
Percutaneous Transseptal Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement System Provides Treatment Option for Patients Who Are Not Candidates for Surgery or TEER
www.newswise.com
Nov. 3, 2025, 9:22 a.m.
Results from a pivotal clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a fully percutaneous transseptal mitral valve replacement (TMVR) procedure in patients with symptomatic, moderate-to-severe mitral regurgitation (MR) who are not candidates for conventional surgery or transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) procedures, demonstrated effective MR reduction with low rates of complications and mortality.
Share on

New Valves Treat ‘No-Option’ Heart Patients
www.medscape.com
Nov. 3, 2025, 9:21 a.m.
In two forms of severe mitral valve disease with high rates of mortality and limited treatment options, multicenter trials with novel transcatheter devices produced what experts described as unprecedented symptom control and rates of survival. The two trials — one directed at severe mitral annular calcifications (MACs) and the other at inoperable severe mitral regurgitation — were conducted without a comparator arm because no meaningful benefit could be expected from alternatives, according to the principal investigators of each trial.
Share on

A doctor's fight to repair, not replace
kevinmd.com
Nov. 3, 2025, 9:19 a.m.
A moment ten years ago struck me hard and has stayed with me ever since. A nineteen-year-old girl had been diagnosed with rheumatic mitral valve disease. Her family was poor, and a friend brought me her scans. I knew I could save her valve and protect her future. No lifelong anticoagulants. No cold ticking in her chest, like a metronome counting down her days. No fear that a stumble on the stairs might turn into a medical emergency. I told her: make the journey at your own expense, and I will perform the surgery for free. But before I could schedule it, another hospital stepped in. They promised to cover all her hospitalization costs, and then replaced her valve with a mechanical one. She survived. But now, she will live the rest of her life with a foreign device inside her, bearing all the risks and sacrifices that come with it.
Share on
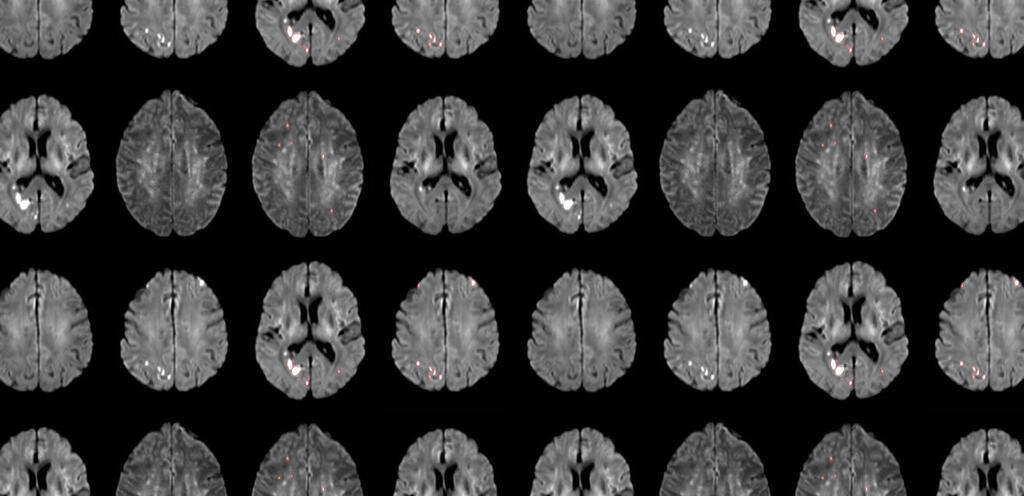
TAVR Procedures Can Cause Brain Injury
protembis.com
Nov. 1, 2025, 4:37 p.m.
Protembis was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in Aachen, Germany. The company develops innovative technologies to reduce the risk of new brain injury during cardiology procedures particularly in connection with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Share on
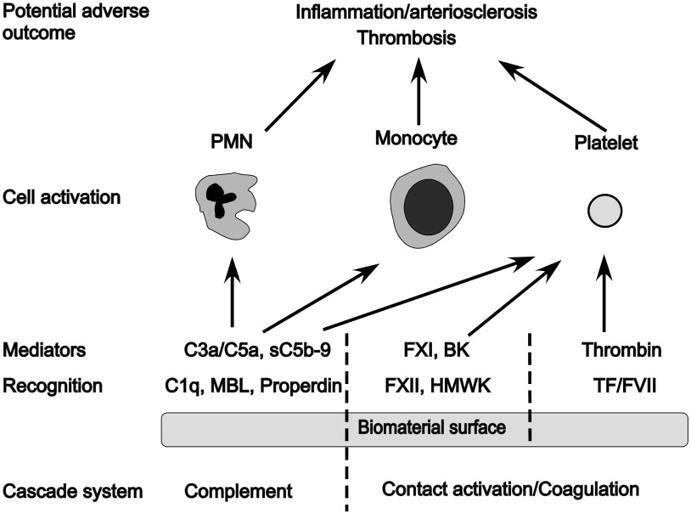
Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: A mechanistic model and coping strategies
www.sciencedirect.com
Sept. 14, 2025, 4:21 a.m.
Overall, considerably more success has been achieved in reducing the thrombogenicity of bio-artificial surfaces than in controlling complement activation: For example, surfaces coated with different forms of heparin or PEG are associated with low or negligible activation of coagulation and subsequent platelet loss. Thus, there are numerous surfaces that have low thrombogenicity available that still bear substantial complement-activating capacity. Some of these materials will no doubt be a
Share on

Transcatheter Aortic Heart Valves: Histological Analysis Providing Insight to Leaflet Thickening and Structural Valve Degeneration
www.jacc.org
Sept. 14, 2025, 3:57 a.m.
There is a time-dependent degeneration of THVs consisting of thrombus formation, endothelial hyperplasia, fibrosis, tissue remodeling, proteinase expression, and calcification. Future investigation is needed to further understand these mechanisms contributing to leaflet thickening and SVD.
Share on

Polymer heart valve, the first of its kind to gain commercial approval, linked to positive 1-year data
cardiovascularbusiness.com
Sept. 14, 2025, 3:52 a.m.
A new-look polymer heart valve is associated with encouraging one-year outcomes in patients undergoing surgical mitral valve replacement (SMVR), according to new data presented at New York Valves 2025 and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.[1]The Tria mitral valve from Utah-based Foldax is built using LifePolymer, a proprietary material that does not include any animal tissue. Both the frame of the valve and its leaflets are robotically generated to match the patient’s native mitral valve.
Share on

Polymeric Heart Valves: Do They Represent a Reliable Alternative to Current Prosthetic Devices?
www.mdpi.com
Sept. 14, 2025, 3:51 a.m.
Prosthetic heart valves are classified as Class III medical devices by the FDA; therefore, they require the highest level of regulatory examination before approval for the market by the competent authorities (e.g., the FDA in the US, notified bodies in the EU). For this purpose, the biggest challenge for PHVs is the successful demonstration of long-term durability in vivo: 10–15 years (or more) can be a reasonable timeframe for approval. Moreover, any new prosthetic device has to exhibit better performance compared to the existing ones and, in the specific case of PHVs, the mechanism of failure has to be precisely addressed. All these issues are particularly challenging!
Share on

Frontiers | Polymeric prosthetic heart valves: A review of current technologies and future directions
www.frontiersin.org
Sept. 14, 2025, 3:48 a.m.
By the year 2050, it is estimated that over 1 million patients will require a heart valve replacement. The available prosthetic valve options that exist today have several limitations including lifelong anticoagulation for mechanical prostheses and structural valve degeneration associated with bioprosthetic valves. Moreover, the costs and materials required to source and process biological tissue limit the widespread utilization of bioprosthetic valves in low-resource settings. Early trials of polymeric heart valves were unsuccessful largely due to a limited ability to modify polymeric compounds to meet the needs of an ideal heart valve substitute. This review describes several advanced polymer technologies that have been incorporated into more recent PHV models.
Share on
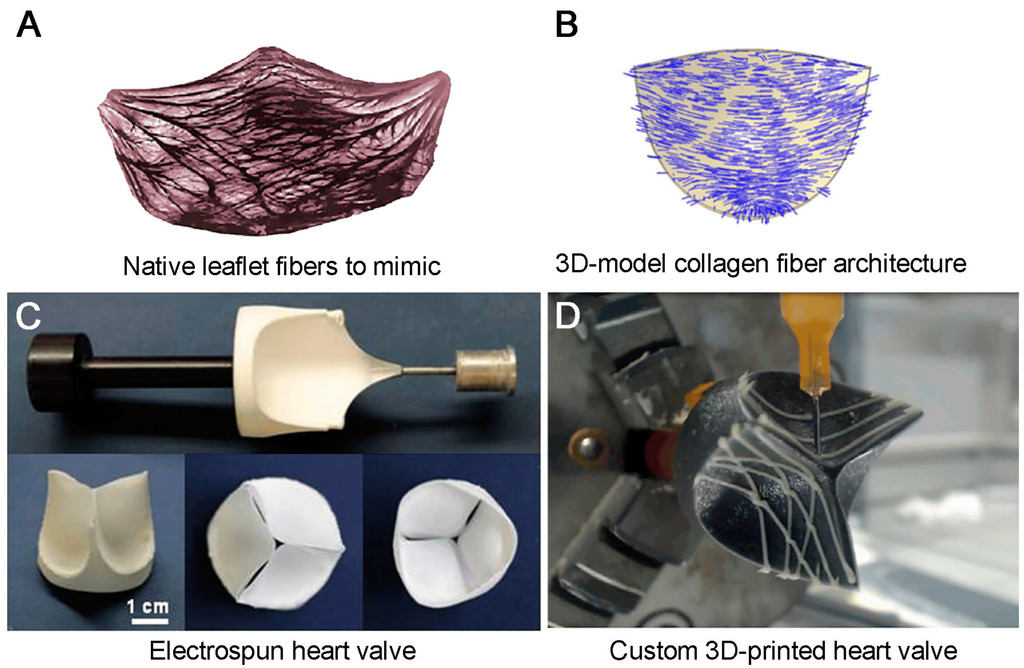
Polymeric Heart Valves Will Displace Mechanical and Tissue Heart Valves: A New Era for the Medical Devices
www.mdpi.com
Sept. 14, 2025, 3:45 a.m.
Currently, the problem of structural valve degeneration can be solved only by using either mechanical or biological prostheses. Despite the wide variety of materials and manufacturing technologies discussed in the review, the advancements in this field are limited by the strict requirements for mechanical properties and biostability, the complex and anisotropic behavior of the valve model, and the lack of self-healing synthetic materials. To date, LifePolymer (Foldax) is the only biopolymer material that has successfully passed preclinical tests and has been implanted in humans during clinical trials. However, in light of recent advances in high-molecular compounds and materials science, especially in the development of various copolymers, nanocomposites, and other hybrid structures combining the advantages of compounds, it has become possible to develop patient-specific anisotropic heart valves. New additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, electrospinning, and microfabrication technologies, have brought the global biomedical community closer to the development of an optimal heart valve prosthesis.
Share on