
PICCOLETO IV trial investigating SAPT after DCB-PCI in high-risk population launches
cardiovascularnews.com
Feb. 23, 2026, 9:05 a.m.
As per international guidelines, coronary lesions are primarily treated with drug-eluting stents (DESs). While DESs have demonstrated good clinical outcomes, even the latest generations remain associated with restenosis, vessel thrombosis, and myocardial infarction (MI), investigators state in a press release. In addition, DES carry an intrinsic thrombotic risk, requiring dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT). However, elderly patients and those at high bleeding risk (HBR) have a cumulative increase in adverse events, including a higher thrombotic risk after angioplasty with DES.
Share on

Invasive and medical management approaches to non-acute myocardial ischaemic syndromes
www.nature.com
Feb. 23, 2026, 9:05 a.m.
The available evidence supports the optimization of medical therapy as the first-line therapeutic approach for most patients with non-acute myocardial ischaemic syndromes.Physicians should carefully consider selected patients who might benefit from invasive therapy with percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Patients with persistent symptoms who are unable to tolerate up-titration of medications might be candidates for early percutaneous coronary intervention to improve symptoms, especially for non-complex coronary artery disease.Selecting appropriate high-risk patients who would benefit from coronary artery bypass graft surgery continues to be supported by the evidence for improved event-free survival.
Share on

Abbott reports positive VERITAS study results for AFib
www.medicaldevice-network.com
Feb. 16, 2026, 9:55 a.m.
According to VERITAS Study data, 93.9% of non-valvular AFib patients implanted with the Amulet 360 achieved full closure of the LAA by 45 days, with no leaks over 3mm. The LAA is a small pouch linked to increased stroke risk in AFib patients. The device is minimally invasive and adapts to each patient’s unique LAA shape, providing immediate closure and potentially reducing the need for blood-thinning medication where suitable.
Share on

Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Drug-Eluting Stents
www.nejm.org
Feb. 16, 2026, 9:51 a.m.
Despite guideline recommendations, evidence for the use of non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant (NOAC) monotherapy in patients with atrial fibrillation after implantation of a drug-eluting stent remains limited.
Share on

MediCoat PSI Peripheral Stent Coating Systems
www.youtube.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 11:45 a.m.
For coating peripheral stents with anti-restenosis drug/polymer solutions. Sono-Tek is well known for providing uniform coatings onto specialty and custom stents with targeted coverage and no webbing.
Share on

Ultrasonic Spraying for Drug-Eluting Stent Coating Preparation
www.youtube.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 11:44 a.m.
Shanghai Yangmi's ultrasonic spraying technology allows for coating thickness deviations within ±5% after deposition onto medical device surfaces. This is particularly suitable for full-coverage coating of complex-shaped medical devices (such as porous stents and threaded implants). It also prevents problems such as solution sedimentation, agglomeration, and uneven atomization during the spraying process.
Share on
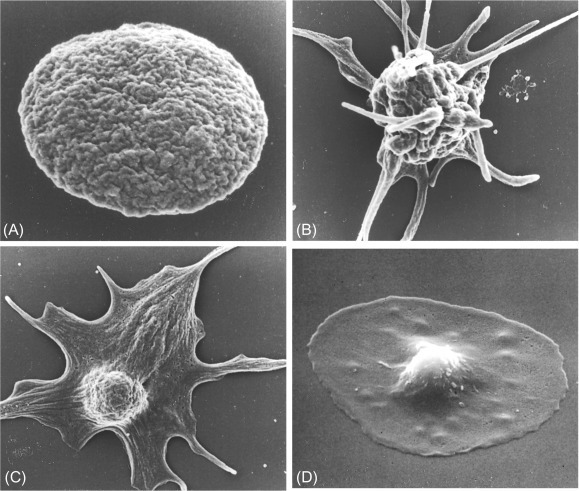
The Structure of Resting and Activated Platelets
www.sciencedirect.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 11:01 a.m.
At first glance, the platelet is a simple cell. However, its small size hides an extremely well conserved structure that is vital for its function in both hemostasis and vascular integrity and development. A combination of electron microscopy, light microscopy, biochemical, and cell biology studies has, over the years, revealed this structure to us and allowed the important functions of the various organelles and subcellular components to be understood. This chapter reviews the structure of the resting platelet and discusses the dramatic and dynamic changes, especially in the cytoskeleton, that occur upon activation to allow platelets to carry out their primary function in hemostasis.
Share on

Novel Anti-Inflammatory Therapies in Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndromes
www.mdpi.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 10:59 a.m.
Inflammation plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis as evidenced by the data of preclinical studies and large epidemiological trials. The pathophysiological association between inflammation and atherosclerosis is very complex and many mediators are included. The most important mediators of this association are the cytokines and, specifically, IL-1β and IL-6 chemokines, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. Large randomized clinical studies and meta-analyses have shown that anti-inflammatory therapies have a favorable efficacy profile and can reduce the hazard of cardiovascular events. However, the results of randomized trials of therapies specifically targeting inflammation are controversial, and, therefore, further studies are needed to elucidate this association in the future.
Share on

Anti-inflammatory therapy with low-dose IL-2 in acute coronary syndromes: a randomized phase 2 trial
www.nature.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 10:58 a.m.
Patients who have residual inflammation following acute coronary syndromes (ACSs) are at high risk of further major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs). Canakinumab and colchicine are anti-inflammatory agents that target the innate immune system and have been shown to reduce MACEs in patients with chronic coronary artery disease. In the ACS population, the evidence for colchicine reducing MACEs has been less robust, with recent data showing that it was ineffective in ACSs. Furthermore, both agents have significant side effects. An unmet clinical need therefore exists to identify a well-tolerated drug that regulates the immune system and effectively reduces residual inflammation in ACSs.
Share on

Revolutionising care: Drug-eluting stent platform designed to address edge restenosis poised to deliver next-generation solution in dialysis access circuit maintenance
vascularnews.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 10:55 a.m.
Effective, durable options to address faltering dialysis access circuits have remained elusive, leaving a significant unmet need in long-term access maintenance. Until now. Promising interim data have emerged from the prospective, multicentre DEScover trial evaluating the Solaris DE sirolimus-eluting, electrospun polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) covered stent for the treatment of failed access circuits, drawing high hopes from leading global vascular specialists that a transformational solution might finally be at hand. “We have never had a drug-eluting platform that directly addressed the issue of edge restenosis, which is where most of these types of devices fail, when they fail,” says Peter Schneider (University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, USA). “This is where the Solaris DE platform will have a big impact—it will be a one-of-a-kind.”
Share on

A novel noble metal stent coating reduces in vitro platelet activation and acute in vivo thrombosis formation
www.nature.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 10:47 a.m.
Inherent to any stenting procedure is the prescription of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) to reduce the platelet response. Clinical guidelines recommend 6–12 months of DAPT, depending on stent type, clinical picture and patient factors. Our hypothesis is that a nanostructured noble metal coating has the potential to reduce protein deposition and platelet activation. These effects would reduce subsequent thrombo-inflammatory reactions, potentially mitigating the need for an extensive DAPT in the acute phase. Here, a noble metal nanostructure coating on stents is investigated. Twelve pigs underwent endovascular implantation of coated and non-coated stents for paired comparisons in a blinded study design.
Share on
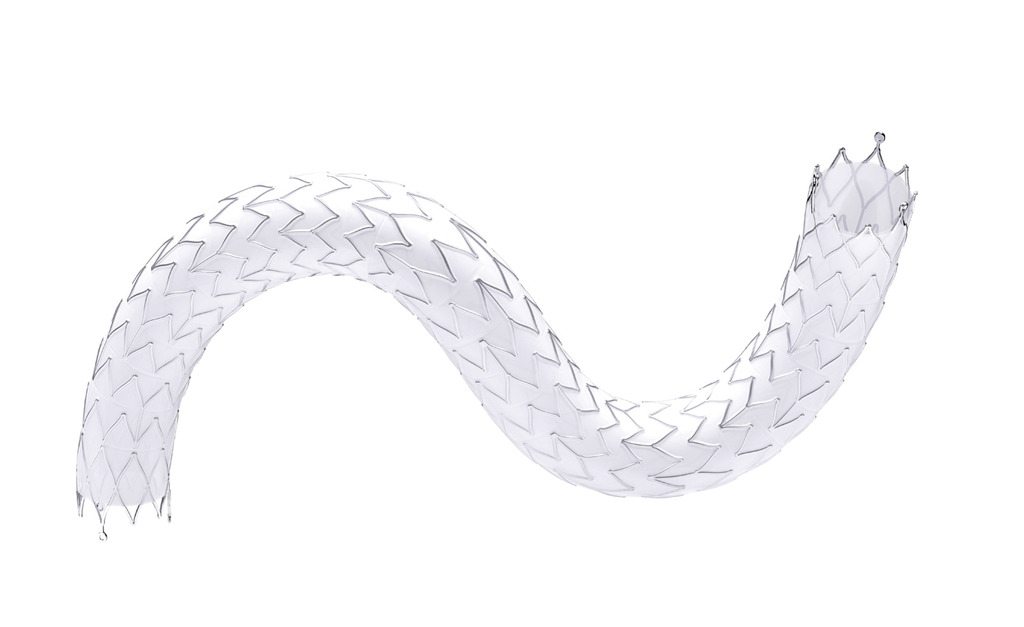
Revolutionising care: Drug-eluting stent platform designed to address edge restenosis poised to deliver next-generation solution in dialysis access circuit maintenance
vascularnews.com
Feb. 2, 2026, 9:39 a.m.
Effective, durable options to address faltering dialysis access circuits have remained elusive, leaving a significant unmet need in long-term access maintenance. Until now. Promising interim data have emerged from the prospective, multicentre DEScover trial evaluating the Solaris DE sirolimus-eluting, electrospun polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) covered stent for the treatment of failed access circuits, drawing high hopes from leading global vascular specialists that a transformational solution might finally be at hand. “We have never had a drug-eluting platform that directly addressed the issue of edge restenosis, which is where most of these types of devices fail, when they fail,” says Peter Schneider (University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, USA). “This is where the Solaris DE platform will have a big impact—it will be a one-of-a-kind.”
Share on

A novel noble metal stent coating reduces in vitro platelet activation and acute in vivo thrombosis formation: a blinded study
www.nature.com
Jan. 29, 2026, 3:47 p.m.
Inherent to any stenting procedure is the prescription of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) to reduce the platelet response. Clinical guidelines recommend 6–12 months of DAPT, depending on stent type, clinical picture and patient factors. Our hypothesis is that a nanostructured noble metal coating has the potential to reduce protein deposition and platelet activation. These effects would reduce subsequent thrombo-inflammatory reactions, potentially mitigating the need for an extensive DAPT in the acute phase. Here, a noble metal nanostructure coating on stents is investigated.
Share on

Optical coherence tomography assessment of a PLGA-polymer with electro-grafting base layer versus a PLA-polymer sirolimus-eluting stent at three-month follow-up: the BuMA-OCT randomised trial
eurointervention.pcronline.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 2:12 p.m.
In the BuMA-OCT randomised trial, the novel BuMA PLGA-polymer with electro-grafting base layer SES was superior to the EXCEL PLA-polymer SES in the primary endpoint of stent strut coverage at three-month follow-up.
Share on

When biology drives benefit: how lesion morphology shapes DCB response
vascularnews.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:37 a.m.
Based on the “strong” results of the IN.PACT AV Access trial across different anatomical regions in native fistulas, he explains, DCBs should be used as “first-line treatment” for stenosis. In his opinion, de novo lesions are the “perfect” place to start DCB treatment, because the paclitaxel has a cytotoxic action for cells in active proliferation.
Share on

Trial of polymer-free DES in STEMI PCI enrols first patients
cardiovascularnews.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:35 a.m.
STARS DAPT aims to study the difference between a P2Y12 receptor inhibitor-based single antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) regimen after a short period of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) versus conventional six or 12 months of DAPT. The co-primary endpoints at 12 months are major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events and major bleeding complications.Newer generation polymer-free DES like the Abluminus np with thin struts, fusion and abluminal coating of Sirolimus aids in natural vascular healing of the arteries, faster re-endothelialisation and mitigating chronic inflammation which permits the possibility of potentially shortening the DAPT requirement, Concept Medical says in a press release. Abluminus np has been studied in single-arm Indian registries with promising safety and efficacy leading up to STARS DAPT being the first randomised evaluation
Share on
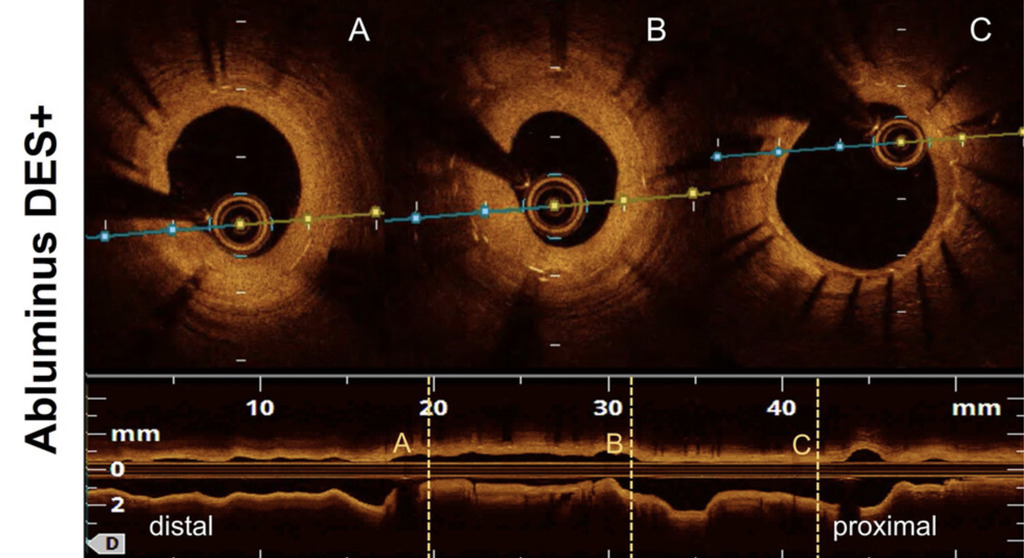
Randomized clinical trial of abluminus DES+ sirolimus-eluting stent versus everolimus-eluting DES for percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with diabetes mellitus: An optical coherence tom...
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:34 a.m.
This preliminary study failed to demonstrate the superiority of the Abluminus DES+ over the DP-EES in diabetic patients in terms of neointimal proliferation.
Share on

Deep Learning–Based Segmentation of Coronary Arteries and Stenosis Detection in X-Ray Coronary Angiography
www.jacc.org
Jan. 8, 2026, 11:28 a.m.
Deep learning applications may assist in automatically detecting coronary arteries on invasive coronary angiography (ICA).
Share on

Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation in Restenosis
www.ahajournals.org
Jan. 8, 2026, 11:27 a.m.
Smooth muscle proliferation and migration after percutaneous intervention represent the end result of natural healing processes triggered by vascular injury. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, especially after stent implantation, plays a critical role in neointimal hyperplasia through cellular expansion and extracellular matrix deposition. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms responsible for smooth muscle cell proliferation has led to the development of novel therapeutic approaches, including rapamycin- and paclitaxel-eluting stents that have significantly improved the care of patients with coronary artery disease. To address the concerns about the potentially increased incidence of stent thrombosis in patients treated with drug-eluting stents, newer stents and coronary devices have been developed such as drug-eluting stents with biodegradable polymers, drug-eluting stents that are polymer-free, stents with novel coatings, completely biodegradable stents, bifurcation stents, and drug-eluting balloons.
Share on

PDGF-induced proliferation in human arterial and venous smooth muscle cells: Molecular basis for differential effects of PDGF isoforms
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Jan. 8, 2026, 11:25 a.m.
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of arterial atherosclerosis and venous neointimal hyperplasia. We examined the effects of PDGF isoforms on smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from arterial and venous origins in order to further understand the differential responsiveness of these vasculatures to proliferative stimuli. Serum-starved human arterial and venous SMCs exhibited very different proliferative responses to PDGF isoforms. Whereas, proliferation of arterial SMCs was strongly stimulated by PDGF-AA, venous SMCs showed no proliferative response to PDGF-AA, but instead demonstrated a significantly greater proliferative response to PDGF-BB than arterial SMCs. Part of this difference could be attributed to differences in PDGF receptors expression.
Share on