
A Giant Left Anterior Descending Artery Aneurysm and an Updated Review on Coronary Aneurysms
www.ajconline.org
July 14, 2025, 10:03 a.m.
Coronary aneurysm is defined as a focal dilation of the coronary artery that is at least 1.5 times the diameter of an adjacent normal segment.1 The term coronary aneurysm is often interchangeably used with coronary ectasia, which is arbitrarily defined as a more diffuse dilation of the coronary artery of the same dimensional features as an aneurysm.2 Coronary aneurysms and ectasia are observed in at least 5% of patients who underwent coronary imaging.3 Given the recent expansive use of noninvasive coronary artery imaging, especially coronary computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance imaging angiography, the detection of coronary aneurysm has become more frequent.4
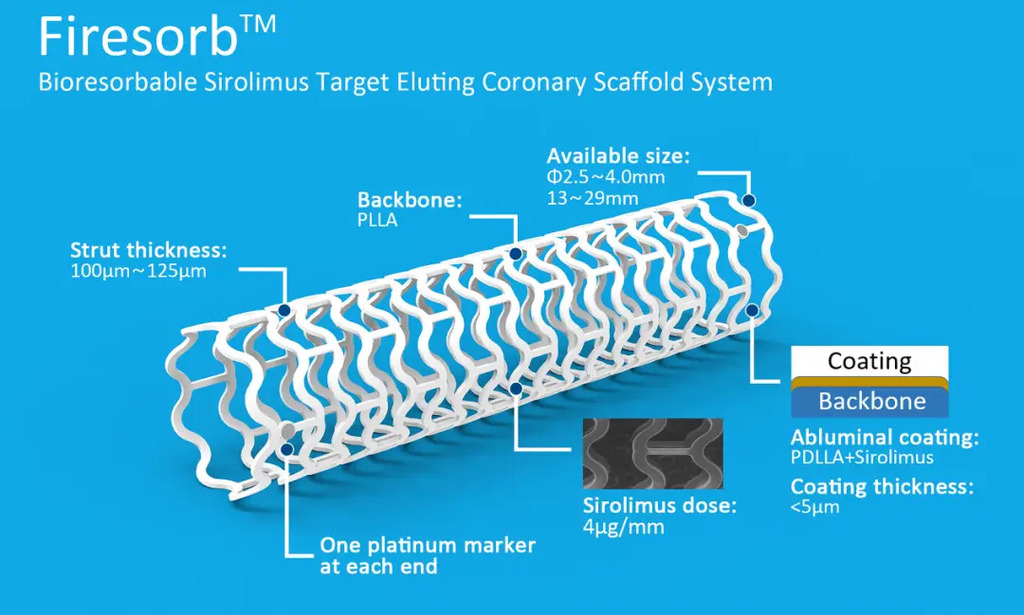
Firesorb bioresorbable scaffold for de novo coronary artery disease: 1-year clinical outcomes
bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com
July 14, 2025, 9:58 a.m.
The first-generation bioresorbable scaffolds (BRS) have been associated with higher rates of device-related adverse outcomes in comparison to everolimus-eluting stents. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the thinner-strut (100/125 μm) poly-L-lactic acid-based sirolimus-eluting Firesorb BRS in patients with de novo coronary lesions.
Share on

Teleflex completes acquisition of Biotronik’s Vascular Intervention business
cardiovascularnews.com
July 7, 2025, 2:29 p.m.
The acquired Vascular Intervention business consists of a portfolio for coronary and peripheral interventions performed in the cath lab and interventional radiology suites. In coronary vascular interventions, Teleflex details that key products include the Pantera Lux drug-coated balloon catheter, the novel PK Papyrus covered coronary stent for acute coronary artery perforations, and the Orsiro Mission drug-eluting stent, an ultrathin drug-eluting stent with differentiated clinical features. For peripheral interventions, the portfolio includes the Passeo-18 Lux peripheral drug-coated balloon catheter, Dynetic-35 balloon-expandable cobalt chromium stent, the Pulsar-18 T3 self-expanding 4F stent, and the Oscar peripheral multifunctional catheter system.
Share on
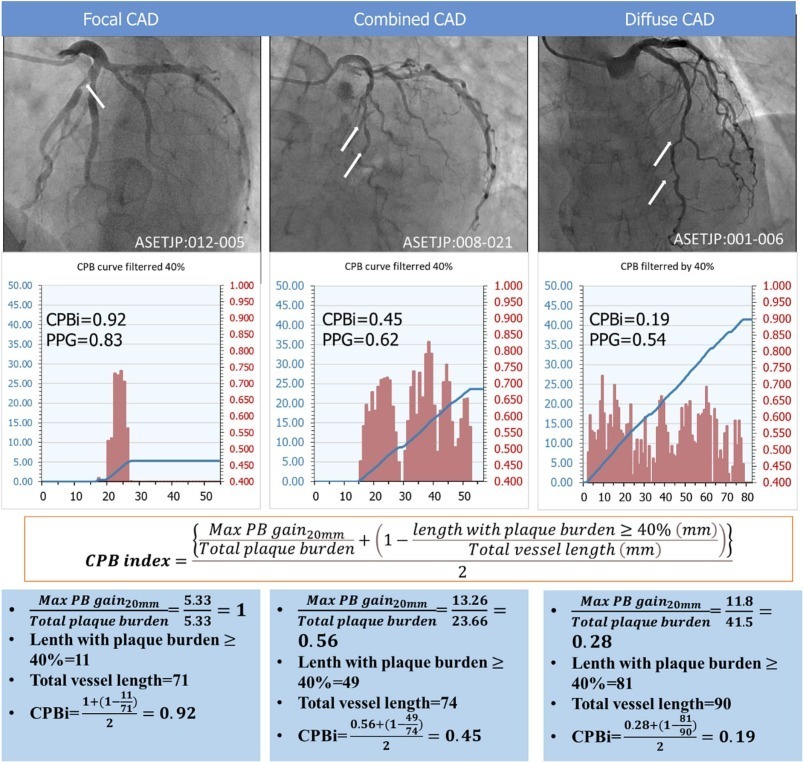
Cumulative Plaque Burden index for determining the diffuseness of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease
www.internationaljournalofcardiology.com
June 30, 2025, 5:31 p.m.
In this study, we propose CPBi, a novel AI-powered IVUS-derived metric, to objectively quantify the diffuseness of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (ACAD) across the entire vessel. This approach provides insight into the distribution of atherosclerosis without requiring hyperemic pressure wire pullback and supports clinical decision-making for optimal stent strategy.
Share on

Leukocyte-shed soluble CD31 unmasks coronary disease in low-risk outliers and provides source-specific inflammatory signatures of vulnerable plaques
www.atherosclerosis-journal.com
June 28, 2025, 10:27 a.m.
Leukocyte-shed sCD31 unmasks coronary disease in low-risk outliers and provides source-specific inflammatory signatures of vulnerable plaques. The differential pattern of sCD31 forms based on risk burden suggests distinct pathophysiological mechanisms driving atherosclerosis in different patient populations, addressing a critical gap in current risk assessment.

Incidence and costs of bleeding-related complications in French hospitals following surgery for various diagnoses
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
June 24, 2025, 8:32 a.m.
This study estimated increases of hospital LOS and costs for patients with severe surgical bleeding complications in France. Hospitalisations longer than the average LOS across all DRGs indicated significant costs associated with severe post-surgical bleeding. Awareness of the clinical and economic consequences of severe post-surgical bleeding provides an important framework when evaluating blood conservation strategies.
Share on
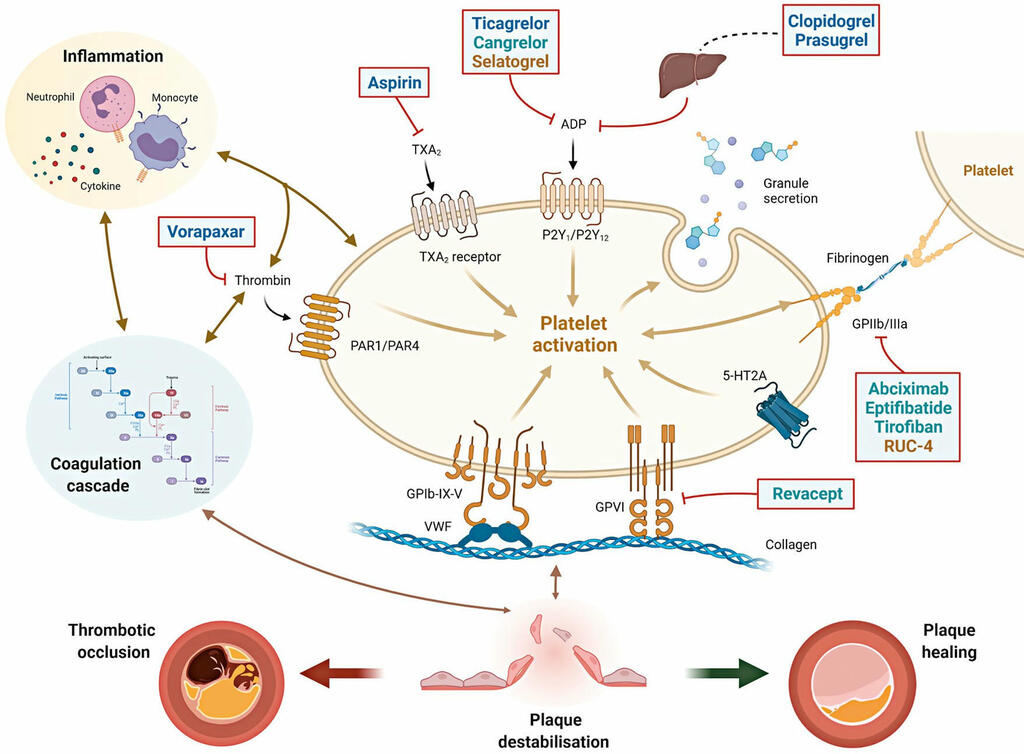
Antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention
eurointervention.pcronline.com
June 24, 2025, 8:03 a.m.
Antiplatelet therapy is key to reducing local thrombotic complications and systemic ischaemic events among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI), but it is inevitably associated with increased bleeding. The continuous refinement in stent technologies, together with the high incidence of ischaemic recurrences after PCI and the understanding of prognostic implications associated with bleeding, have led to a substantial evolution in antiplatelet treatment regimens over the past decades.
Share on
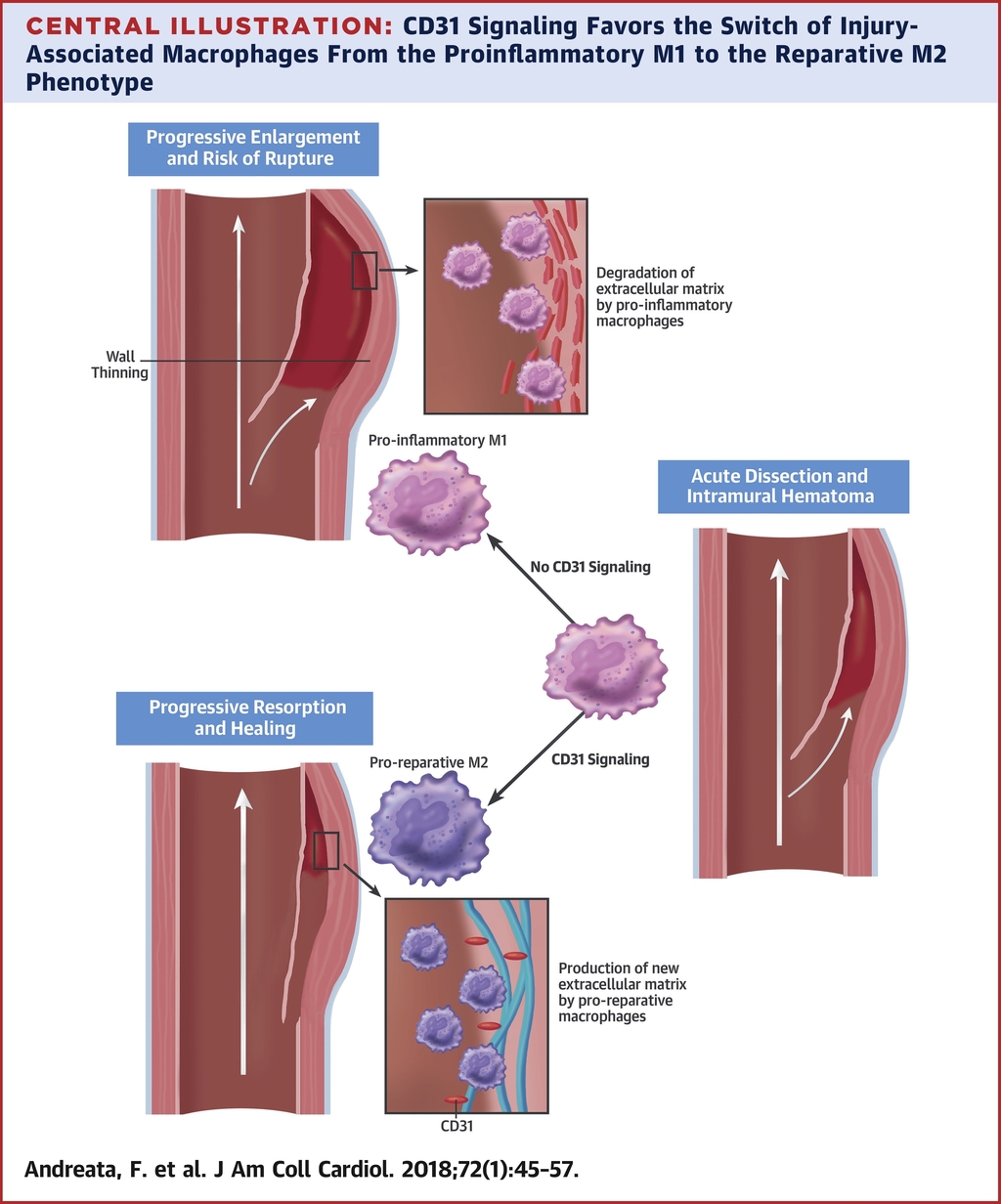
Macrophage CD31 Signaling in Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm
www.jacc.org
June 18, 2025, 1 p.m.
CD31 signaling promotes the switching of proinflammatory macrophages to the reparative phenotype and favors the healing of experimental dissected aortas. Treatment with a drug-suitable CD31 agonist may facilitate the clinical management of ADIM.
Share on

Trial of DCB and scaffold technologies enrols first CTO-PCI patients
cardiovascularnews.com
June 14, 2025, 12:40 p.m.
Biotronik has announced the enrolment of the first patient in the Leave Nothing Behind-trial, which aims to demonstrate the non-inferiority of drug-coated balloons (DCB) or DCBs in combination with resorbable magnesium scaffolds (RMS) compared to drug-eluting stents (DES) in chronic total occlusions (CTO) in percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI).
Share on
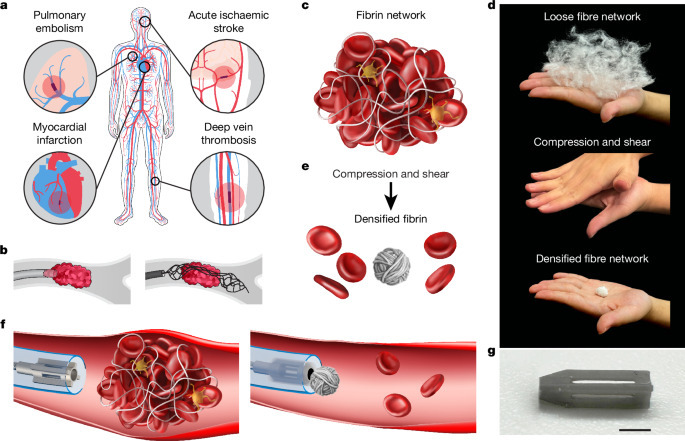
Milli-spinner thrombectomy
www.nature.com
June 14, 2025, 12:39 p.m.
Clot-induced blockage in arteries or veins can cause severe medical conditions. Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive technique used to treat ischaemic stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism and peripheral vascular disease by removing clots through aspiration, stent retriever or cutting mechanisms. However, current mechanical thrombectomy methods fail to remove clots in 10–30% of patients, especially in the case of large, fibrin-rich clots. These methods can also rupture and fragment clots, causing distal emboli and poor outcomes. To overcome these challenges, we develop the milli-spinner thrombectomy, which uses a simple yet innovative mechanics concept to modify the clot’s microstructure, facilitating its removal.
Share on

P2Y12 inhibitor or aspirin after percutaneous coronary intervention
www.bmj.com
June 14, 2025, 12:33 p.m.
In patients who had undergone PCI and discontinued DAPT, at a follow-up of about 5.5 years, P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy with ticagrelor or clopidogrel was associated with lower MACCE, owing to reduced rates of myocardial infarction and stroke compared with aspirin monotherapy, without a concurrent increased risk of major bleeding.
Share on
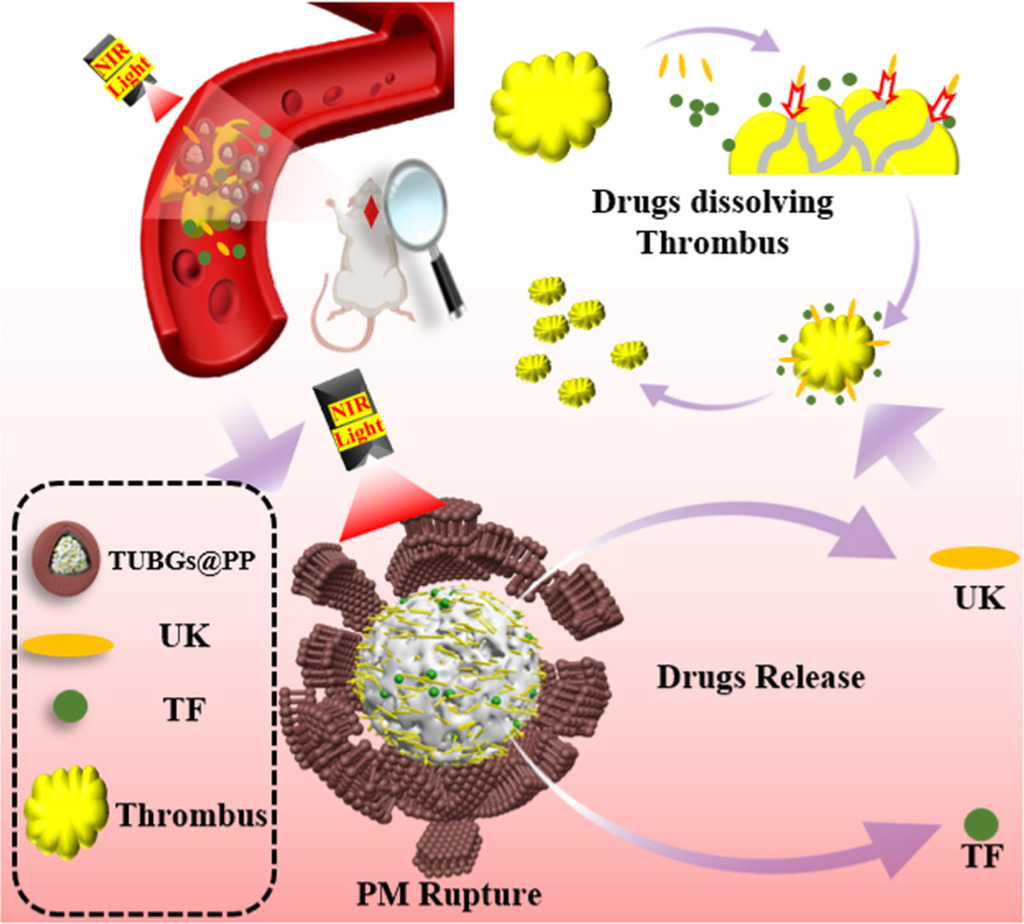
Platelet membrane-camouflaged bioactive glass nano-formulations for enhanced drug delivery in the treatment of acute arterial thrombosis
www.sciencedirect.com
June 14, 2025, 9:21 a.m.
Thrombus treatment remains a significant challenge, primarily due to factors such as the short half-life of thrombolytic agents, suboptimal drug utilization, and limited therapeutic efficacy. In this study, we developed a platelet membrane-camouflaged bioactive glass nanoparticles (BGs) as drug carriers to load thrombolytic agent urokinase (UK) and anticoagulant drug tirofiban (TF).
Share on
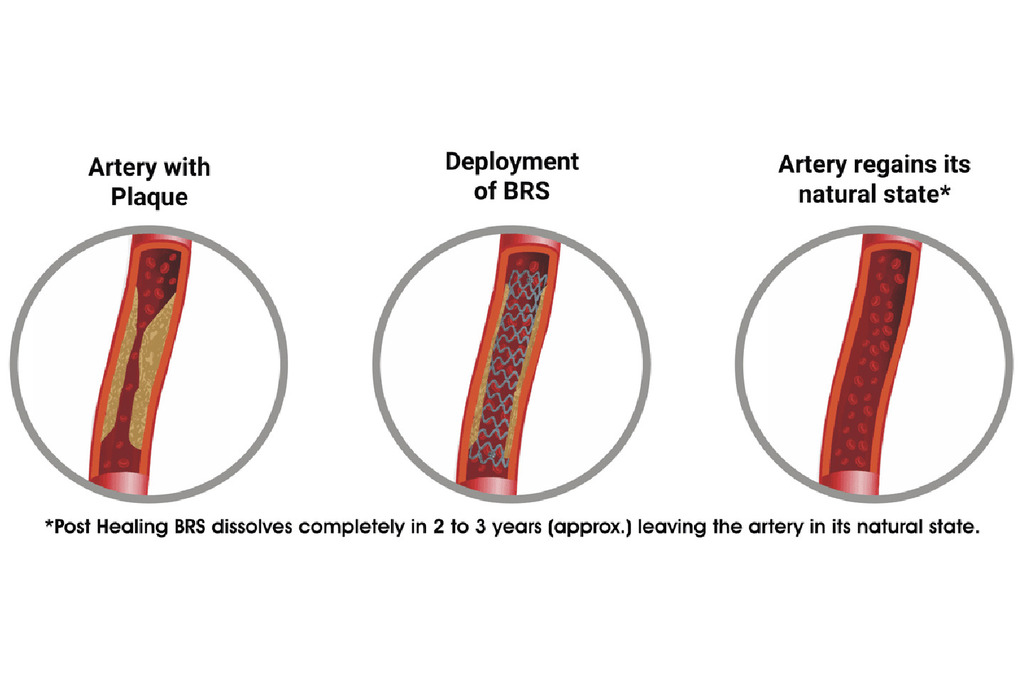
From plumbers to vascular restorers: has the Promethean promise of bioresorbable coronary scaffolds yet to be fulfilled?
eurointervention.pcronline.com
June 7, 2025, 6:10 p.m.
The arrival of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) in the clinical arena was heralded by an impressive list of promises which, in the end, led to a declaration that the fourth revolution in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had taken place1. The reasons for that announcement were sound: it was expected that BVS would put an end to the problem of stent thrombosis and other vascular issues associated with leaving behind a metallic cage once the stenosis had been successfully resolved.
Share on
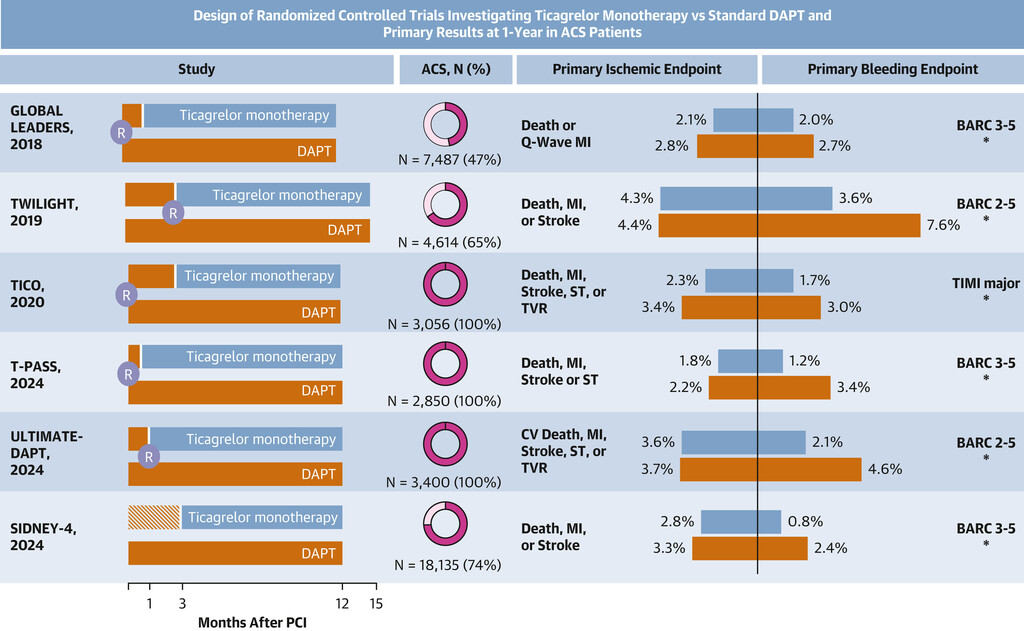
The 2025 ACS Guideline Update Endorses Ticagrelor Monotherapy ≥1 Month After DAPT Post-PCI: The Unbearable Lightness of Ticagrelor Monotherapy
www.jacc.org
June 6, 2025, 9 a.m.
The 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI Guideline for the Management of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) introduced a paradigm shift in secondary prevention by endorsing ticagrelor monotherapy after ≥1 month of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) as a Class 1 (Level of Evidence: A) recommendation for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).1 This endorsement is likely to raise debate because P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy trials have been criticized for design heterogeneity, a predominant focus on bleeding, and noninferiority frameworks for ischemic outcomes. This recommendation is nonetheless supported by a strong rationale and robust clinical evidence, challenging the long-established 12-month DAPT dogma and, more broadly, the necessity of prolonged DAPT when alternative strategies that balance bleeding risk and ischemic protection are available.
Share on
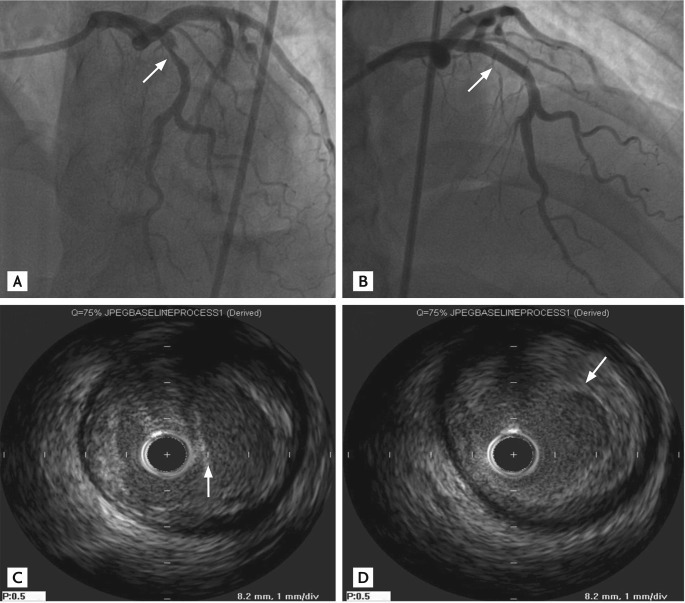
Rethinking Coronary Dissections in Drug-coated Balloon Angioplasty – A Paradigm Shift
www.ajconline.org
May 26, 2025, 11:12 a.m.
The increasing adoption of drug-coated balloons (DCBs) in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) represents a significant shift in interventional cardiology. While experienced operators perceive this as a revival of a familiar technique, newer generations remain skeptical. The concept of leaving a dissection 'uncovered' contradicts the longstanding practice of routine stenting of dissections, a gold standard in PCI for nearly three decades. Concerns regarding abrupt vessel occlusion, increased restenosis, and target lesion failure fuel skepticism.
Share on
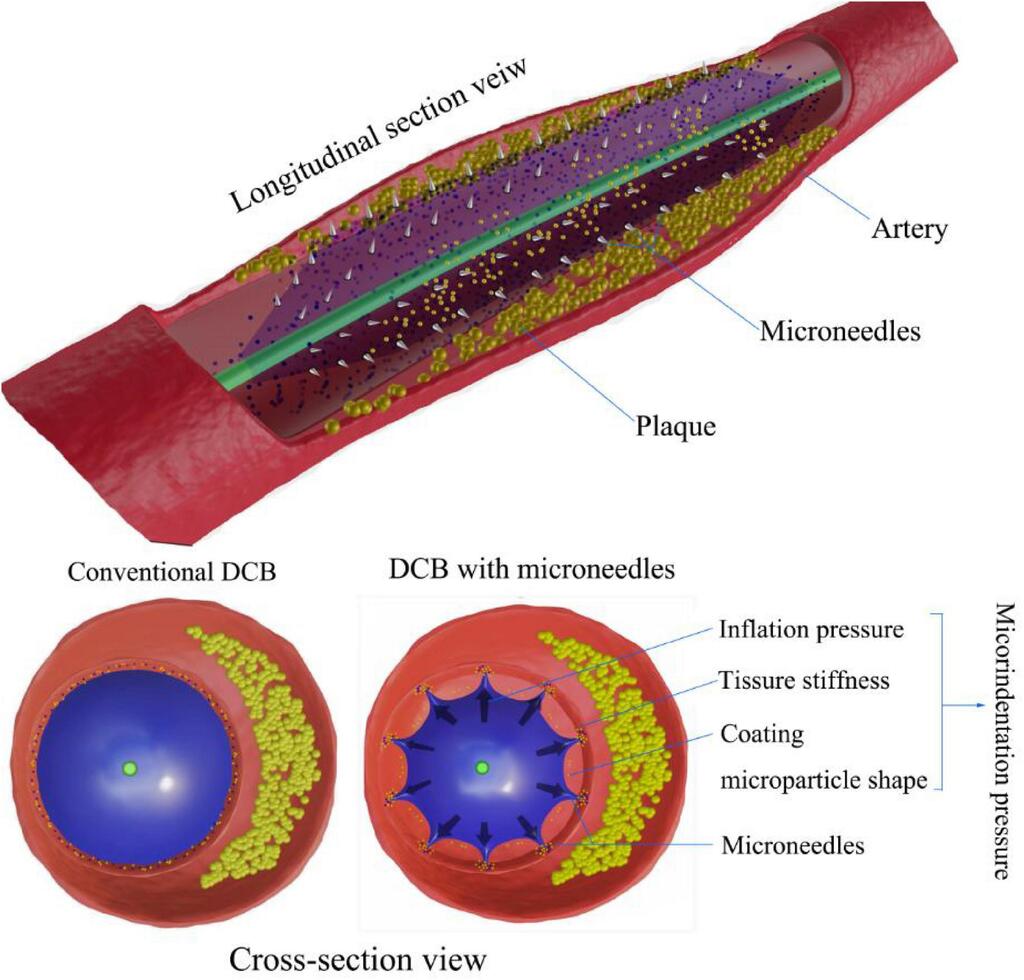
The factors influencing the efficiency of drug-coated balloons
www.frontiersin.org
May 26, 2025, 11:11 a.m.
The drug-coated balloon (DCB) is an emerging percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) device that delivers drugs to diseased vessels to decrease the rate of vascular stenosis. Recent clinical studies have demonstrated that DCBs tend to have both good safety and efficacy profiles, leading to extended application indications in the clinic, including in-stent restenosis (ISR) for metal stents such as drug-eluting stents (DESs), small vascular disease, bifurcation disease, large vascular disease, acute coronary syndrome (ACS), and high bleeding risk. However, some previous clinical data have suggested that DCBs performed less effectively than DESs. No studies or reviews have systematically discussed the improvement strategies for better DCB performance until now. Drug loss during the process of delivery to the target lesion and inefficient delivery of the coating drug to the diseased vascular wall are two key mechanisms that weaken the efficiency of DCBs.
Share on

Stepwise dual antiplatelet therapy de-escalation in patients after drug coated balloon angioplasty (REC-CAGEFREE II)
www.bmj.com
May 19, 2025, 7:42 a.m.
Among participants with acute coronary syndrome who could be treated by drug coated balloons exclusively, a stepwise DAPT de-escalation was non-inferior to 12 month DAPT for net adverse clinical events.
Share on
Japanese Scientists Created Universal Artificial Blood
www.healthcarepackaging.com
May 18, 2025, 8:39 p.m.
The artificial blood could be a game-changer for blood transfusions as it can safely be administered to all patients regardless of blood type.
Share on
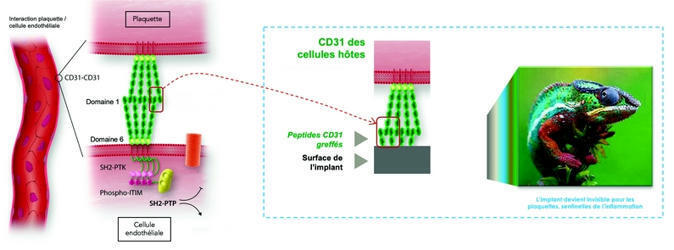
Un revêtement qui mime l’endothélium pour camoufler les stents –
www.devicemed.fr
May 15, 2025, 8:40 a.m.
Essaimage du CEA, la société AlchiMedics développe un revêtement biomimétique destiné aux implants endovasculaires. Cette innovation majeure, qui est le fruit de travaux de recherche menés à l'Inserm, devrait apporter une solution durable à une problématique persistante depuis plus de 25 ans.
Share on

CABG Still Superior to Stents Despite FAME 3 Endpoint Swap
www.medscape.com
May 12, 2025, 6:45 a.m.
While PCI and CABG have improved over time, CABG remains the superior strategy in patients with multivessel disease. The findings for FAME 3 at 5 years are no different from the 1-year outcomes. The only change has been in how the authors presented the results.
Share on