
A phase I-II study of niacin in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: safety and interim phase II analysis
link.springer.com
Feb. 16, 2026, 9:56 a.m.
Survival of patients with glioblastoma (GB) treated with standard of care (SOC) surgery, radiotherapy, and temozolomide is 15 months with progression free survival at 6 months (PFS-6 M) of 53.9%. In vivo studies showed increased survival in mice with GB treated with niacin. This is a first in human Phase I-II study aiming to evaluate safety and efficacy of controlled-release niacin (NiacinCRT ™) added to SOC.
Share on
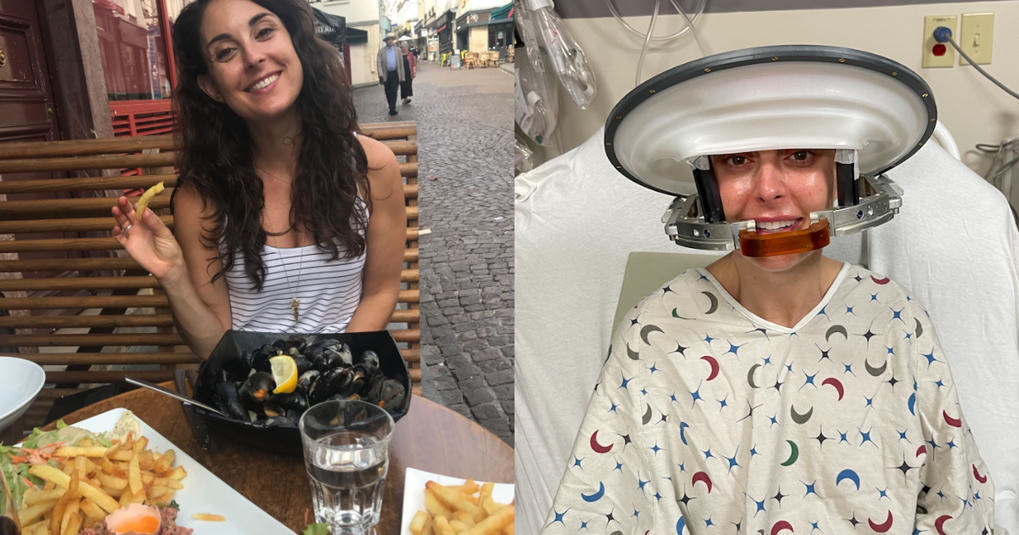

Woman shares unlikely survival journey after migraines led to glioblastoma diagnosis: "I am truly an outlier"
www.cbsnews.com
Feb. 15, 2026, 11 a.m.
Valle said she had no side effects from participating in the trial. Four years after her diagnosis with glioblastoma, she has no evidence of disease. It's a rare positive outcome for a disease that kills most patients within 18 months. "I am truly an outlier," Valle, now 41, said.
Share on
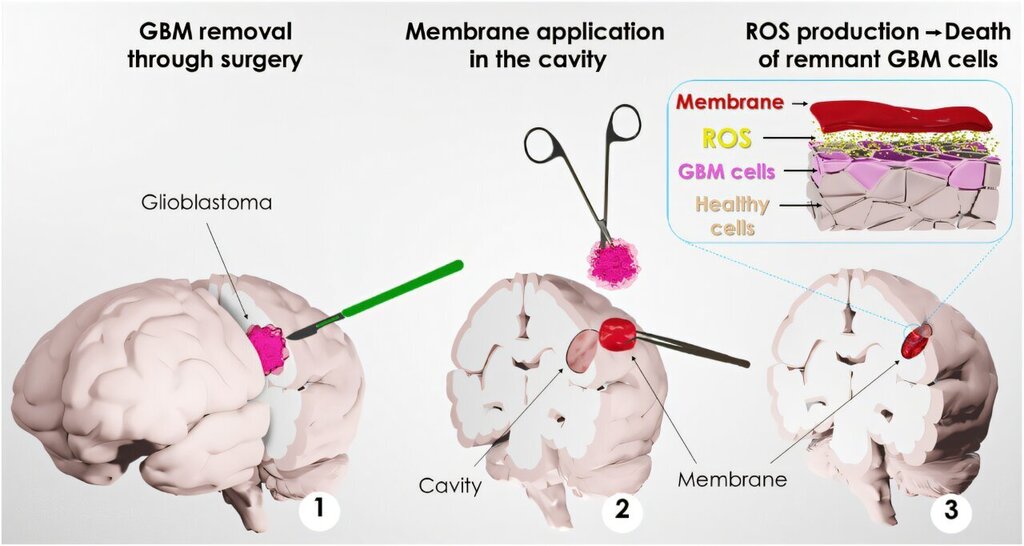
A Mussel-Inspired Bioadhesive Patch to Selectively Kill Glioblastoma Cells
advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Feb. 9, 2026, 8:13 a.m.
Our work introduces for the first time the use of novel bioinspired membranes designed as a potential patch platform for localized intervention in glioblastoma after surgery, representing a promising advancement in this field. Despite the rapid growth in mussel-inspired research, this work is distinctly innovative. Unlike the common hydrogel and coatings focus, our solid, free-standing bioadhesive membranes could offer a unique solution for glioblastoma treatment. Moreover, their selective toxicity against cancer cells, while sparing healthy astrocytes in vitro, highlights their potential for a novel and targeted application. Our bioinspired membrane addresses critical challenges such as adhesion in humid environments, infection prevention, and biocompatibility. The adhesive properties of the membrane ensure it stays in place, allowing for the sustained delivery of the localized cytotoxic effect to the affected area. This novel approach offers a localized and sustained therapeutic concept based on ROS modulation, that could complement the current glioblastoma treatment paradigm.
Share on

Taming Tumor Chaos: Researchers Uncover Key to Improving Glioblastoma Treatment
neurosciencenews.com
Feb. 2, 2026, 9:48 a.m.
When glioblastoma tumors are treated with chemotherapy, levels of miR-181d drop. This drop amplifies the differences among individual cells within the tumor, thereby allowing more cells to make more MGMT and survive treatment. The research team found that administering miR-181d into the tumor can reduce this effect, making the cancer cells behave more uniformly, and importantly, more likely to respond to chemotherapy.
Share on

Tumor-associated macrophage-related strategies for glioma immunotherapy | npj Precision Oncology
www.nature.com
Jan. 31, 2026, 11:32 a.m.
High-grade glioma is one of the deadliest primary tumors of the central nervous system. Despite the many novel immunotherapies currently in development, it has been difficult to achieve breakthrough results in clinical studies. The reason may be due to the suppressive tumor microenvironment of gliomas that limits the function of specific immune cells (e.g., T cells) which are currently the primary targets of immunotherapy. However, tumor-associated macrophage, which are enriched in tumors, plays an important role in the development of GBM and is becoming a research hotspot for immunotherapy. This review focuses on current research advances in the use of macrophages as therapeutic targets or therapeutic tools for gliomas, and provides some potential research directions.
Share on
Glioblastoma Is the Most Aggressive Brain Cancer and May One Day Be Treated With a Common HIV Drug
www.discovermagazine.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:40 a.m.
Ongoing research is trying to change that. A team of scientists from McMaster University and the Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) in Canada has now identified an inconspicuous type of brain cell that reprograms its communication to support glioblastoma growth. When knocked out in experiments, cancer growth slowed down.Not only did they discover a critical role for a brain cell type previously thought to be harmless in cancer development, but they also matched it with a drug already on the market. According to the study published in Neuron, the approved HIV medicine Maraviroc extended the lifespan of mice with glioblastoma, demonstrating that the researchers uncovered a potential target to treat a devastating disease.
Share on
Determinants of survival after re-resection for recurrent glioblastoma: a meta-analysis
www.neurosurgery-blog.com
Jan. 26, 2026, 8:39 a.m.
This systematic review and meta-analysis examines prognostic factors affecting survival after re-resection for recurrent glioblastoma, synthesizing data from 30 studies (1,741 pooled patients). Key findings identify gross total resection and MGMT promoter methylation as strong positive predictors, while age and low preoperative KPS associate with poorer outcomes; adjuvant therapies and time to re-resection showed inconsistent effects.
Share on

Bevacizumab enhances overall survival in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients with high COX-2 expression
www.nature.com
Jan. 12, 2026, 9:46 a.m.
Bevacizumab (BEV) is known to improve progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS) for newly diagnosed glioblastoma (ndGBM). Here, we evaluated the survival outcomes between temozolomide (TMZ)-only and TMZ + BEV treatments stratified based on the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, a rate-limiting enzyme involved in the cancer development.
Share on
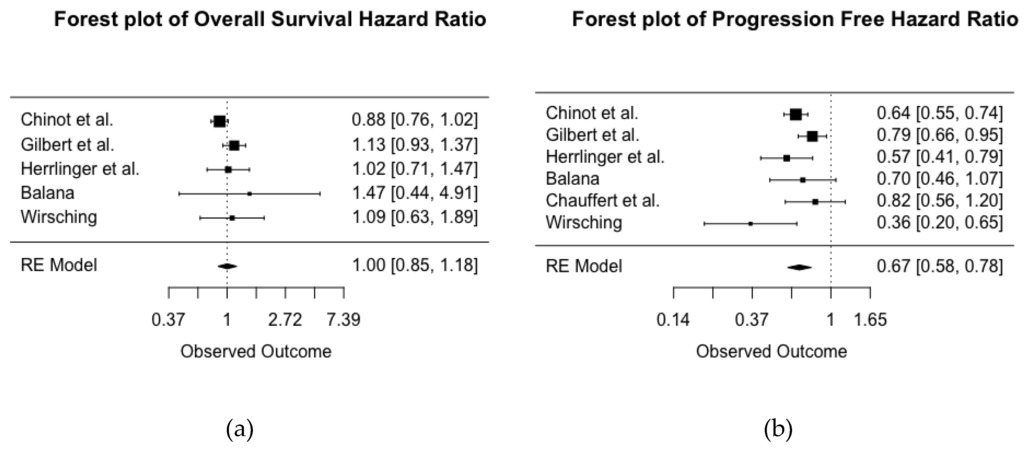
Progression-Free but No Overall Survival Benefit for Adult Patients with Bevacizumab Therapy for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
www.mdpi.com
Jan. 12, 2026, 9:43 a.m.
Despite the limitations of this study, these findings enable evidence-based decision making regarding the use of BEV for the treatment of newly diagnosed GBM. Our study confirms the previous literature concluding that BEV therapy is associated with a prolonged PFS in adult patients diagnosed with newly diagnosed GBM, but has an inconsistent effect on OS. Future research is necessary to define a patient population for whom BEV therapy at diagnosis is indicated.
Share on

Combinatorial treatment of glioblastoma with temozolomide (TMZ) plus 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU)
www.pnas.org
Jan. 5, 2026, 11:44 a.m.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a devastating disease with limited treatment options. We find that EdU in combination with the currently used anticancer drug TMZ produces highly significant survival benefits and synergistic effects in preclinical GBM models. This striking effect presumably results from simultaneously engaging distinct DNA repair pathways and offers a potential tool against this disease.
Share on

Craniopharyngioma – What’s next
link.springer.com
Dec. 20, 2025, 5:52 p.m.
Management of hypothalamic syndrome remains highly challenging. Recently, a risk-adapted, personalized treatment algorithm has been proposed to guide clinical care. Therapeutic interventions such as dextroamphetamine and other centrally acting stimulants, along with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists, and setmelanotide have shown potential in promoting weight reduction. Bariatric surgery has also demonstrated efficacy; however, the use of irreversible surgical techniques in pediatric populations remains ethically and legally contentious. This report summarizes perspectives of future research and clinical progress in diagnostics, treatment, and follow-up of patients with craniopharyngioma.
Share on

Cancer du sein : une thérapie CAR-T de nouvelle génération pourrait changer la donne
archipeldessciences.wordpress.com
Dec. 20, 2025, 5:48 p.m.
Des chercheurs ont développé une thérapie CAR-T à base de cellules tueuses naturelles (« natural killer », NK), qui s’est montrée plus efficace que les immunothérapies actuelles contre le cancer du sein triple négatif à un stade avancé – la forme la plus agressive de cancer du sein. La thérapie peut être produite en masse à partir de dons de cellules souches sanguines, ce qui réduirait considérablement son coût de développement. Sa polyvalence permettrait aussi de l’utiliser contre d’autres types de tumeurs solides.
Share on
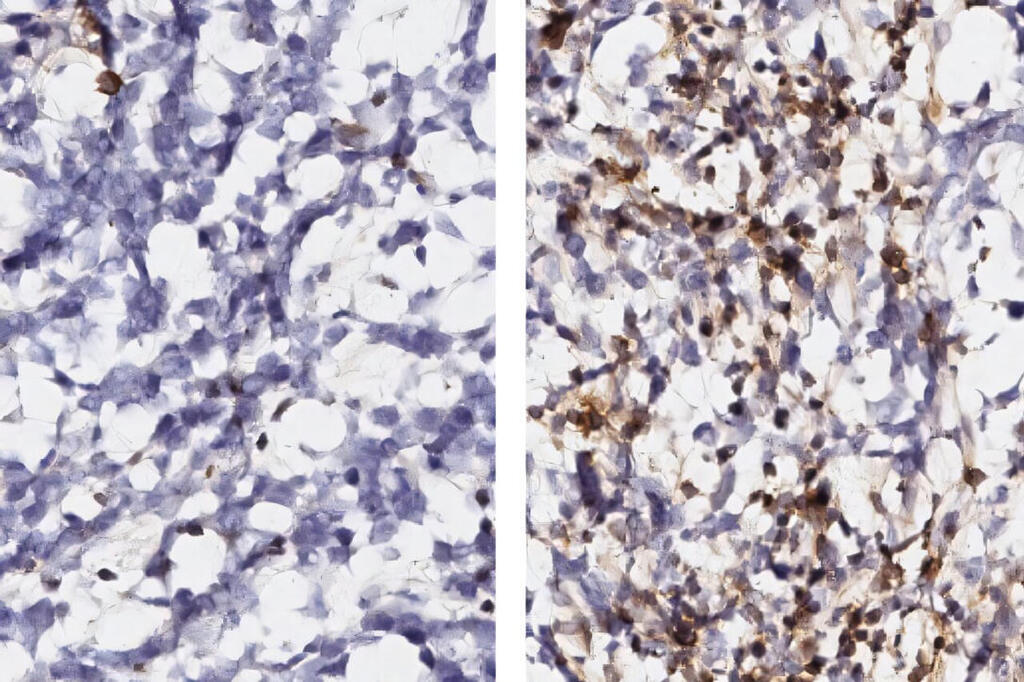
New immunotherapy targets for glioblastoma identified by mapping cell interactions
medicalxpress.com
Dec. 15, 2025, 10:50 a.m.
Glioblastoma is unusually resistant to attack by T cells, rendering immune checkpoint inhibitors ineffective. The culprit is a different immune cell, macrophages, which have been recruited to tumors, where they support tumor growth while suppressing the ability of T cells to infiltrate and attack tumors. A team of researchers led by Forest White at the MIT Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research used sophisticated immune profiling tools to map out how macrophages evolve from a first-line defense against cancer and other pathogens into a shield that protects the glioblastoma tumor—as well as how the tumor cells themselves are transformed by the encounter.
Share on

Modified herpes virus helps destroy glioblastoma in preclinical models
medicalxpress.com
Dec. 8, 2025, 9:27 a.m.
To overcome the barriers, researchers modified an HSV-1 virus to recognize markers found only on glioblastoma cells. They engineered the virus to express five different immunomodulatory molecules to help reprogram the tumor environment, including IL-12, anti-PD1, a bispecific T cell engager, 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase and anti-TREM2.Researchers also added safety mutations, or "off-switches," that prevent the virus from spreading to neurons or healthy central nervous system cells. So that the reach of the virus could be visualized on PET scan, the team inserted a gene that expresses a protein capable of trapping a PET-tracer molecule.
Share on
Retargeted oncolytic viruses engineered to remodel the tumor microenvironment for glioblastoma immunotherapy
www.nature.com
Dec. 8, 2025, 9:25 a.m.
A single intratumoral injection increased survival in GBM preclinical models, while promoting tumor-specific T cell, natural killer cell and myeloid cell responses in the TME. In summary, we engineered a retargeted, safe and traceable oncolytic virus with strong cytotoxic and immunostimulatory activities for GBM immunotherapy.
Share on

Craniopharyngioma – What’s next?
link.springer.com
Dec. 5, 2025, 6:44 p.m.
Professional expertise and the implementation of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic technologies significantly influence the prognosis of patients with CP. Establishing multicenter reference networks is essential to ensure standardized, high-quality treatment protocols and access to specialized care. Future efforts to improve clinical outcomes and quality of life in CP should prioritize an enhanced understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of the disease. This knowledge will be pivotal for the development of targeted therapies that effectively address tumor progression and hypothalamic involvement. Parallel advancements in surgical and radio-oncological techniques should focus on hypothalamus-sparing strategies, minimizing long-term neuroendocrine and metabolic sequelae. Additionally, there is a critical need for policy-level initiatives aimed at defining and implementing quality criteria for multidisciplinary CP management.
Share on

Evaluating the role of stereotactic radiosurgery in craniopharyngioma management
www.news-medical.net
Dec. 5, 2025, 6:42 p.m.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a cornerstone in the multidisciplinary management of craniopharyngioma, particularly for residual or recurrent disease. It offers high rates of tumor control with a favorable toxicity profile compared to conventional radiotherapy. Ongoing technical refinements, combined with molecular insights and personalized treatment planning, promise to further improve outcomes and quality of life for patients with this challenging tumor.
Share on

Focused ultrasound combined with chemotherapy improves survival in glioblastoma patients
www.news-medical.net
Nov. 30, 2025, 9:07 p.m.
Patients with the deadliest form of brain cancer, glioblastoma, who received MRI-guided focused ultrasound with standard-of-care chemotherapy had a nearly 40 percent increase in overall survival in a landmark trial of 34 patients led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers. This is the first time researchers have demonstrated a potential survival benefit from using focused ultrasound to open the blood-brain barrier to improve delivery of chemotherapy to the tumor site in brain cancer patients after surgery.
Share on

Intranasal nanomedicine shows promise against glioblastoma
www.news-medical.net
Nov. 24, 2025, 10:55 a.m.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, along with collaborators at Northwestern University, have developed a noninvasive approach to treat one of the most aggressive and deadly brain cancers. Their technology uses precisely engineered structures assembled from nano-size materials to deliver potent tumor-fighting medicine to the brain through nasal drops. The novel delivery method is less invasive than similar treatments in development and was shown in mice to effectively treat glioblastoma by boosting the brain's immune response.
Share on

Glioblastoma immunotherapy trial: a new breakthrough
kevinmd.com
Nov. 24, 2025, 10:55 a.m.
Kayvon is the first person in the world to undergo natural killer (NK) immunotherapy as part of a clinical trial while also using the Optune Gio device, an electric field-generating device that is worn on the scalp and emits an electromagnetic field into the brain that has been found to disrupt cancer cell division. This innovative approach to an already innovative treatment option has produced results that are so positive, Hoag in Newport Beach, California, is now launching an extension of this phase 2, randomized clinical trial. The hope is that not only will more people benefit from this new approach, but that it will set a new standard of care for this rare but incurable cancer.
Share on